Page 300 - Modern Optical Engineering The Design of Optical Systems
P. 300
Principles of Radiometry and Photometry 279
in Sec. 12.6, this concept is quite useful in evaluating the illumination
at an image point; here we find that it occasionally can be applied to
points which are not image points.
The beam candle power of a searchlight is simply the intensity of the
(point) source which would produce the same illumination at a great
distance. A point source with an intensity of I candles will emit I lumens
per steradian. A one-square-foot area placed d feet from the point
2
source will subtend 1/d steradians from the source, and will thus be
2
illuminated by I/d lumens per square foot (footcandles). We can
determine the necessary candle power for I by equating this illumina-
tion to that produced by the searchlight according to Eq. 12.22.
I TB (lens area)
E (12.23)
d 2 d 2
and beam candlepower:
I TB (lens area)
where I is the beam candle power in lumens per steradian (or candles).
Note that the lens area should be specified in the same units as the
source brightness.
Projection condenser
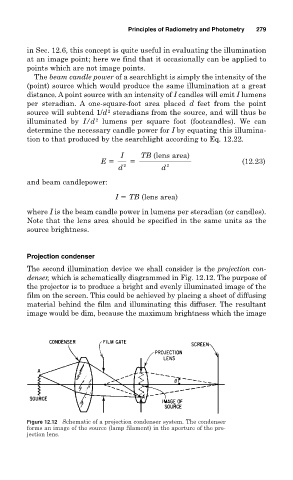
The second illumination device we shall consider is the projection con-
denser, which is schematically diagrammed in Fig. 12.12. The purpose of
the projector is to produce a bright and evenly illuminated image of the
film on the screen. This could be achieved by placing a sheet of diffusing
material behind the film and illuminating this diffuser. The resultant
image would be dim, because the maximum brightness which the image
Figure 12.12 Schematic of a projection condenser system. The condenser
forms an image of the source (lamp filament) in the aperture of the pro-
jection lens.