Page 197 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 197
190 Multidimensional Chromatography
polarity. Fully off-line separation (Figure 8.18(b)), in which several samples are
applied, is complete when the -front of the mobile phase reaches the end of the bot-
tom plate. Figure 8.18(c) illustrates the fully on-line operating mode, in which all the
compounds of the (single) sample to be separated have to be moved at the same sep-
aration distance. The mobile phase can therefore be directed from the lower plate in
a manner similar to that in which it is introduced. This gives the possibility of on-line
detection. For this fully on-line mode of operation, the length of all layers placed
between the uppermost and lowest plates must be reduced by 1 cm, in order to
ensure room for the mobile phase outlet.
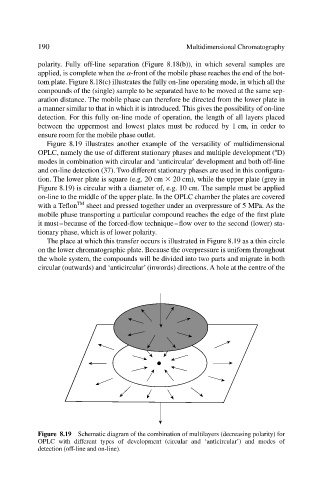
Figure 8.19 illustrates another example of the versatility of multidimensional
n
OPLC, namely the use of different stationary phases and multiple development ( D)
modes in combination with circular and ‘anticircular’ development and both off-line
and on-line detection (37). Two different stationary phases are used in this configura-
tion. The lower plate is square (e.g. 20 cm 20 cm), while the upper plate (grey in
Figure 8.19) is circular with a diameter of, e.g. 10 cm. The sample must be applied
on-line to the middle of the upper plate. In the OPLC chamber the plates are covered
with a Teflon TM sheet and pressed together under an overpressure of 5 MPa. As the
mobile phase transporting a particular compound reaches the edge of the first plate
it must–because of the forced-flow technique–flow over to the second (lower) sta-
tionary phase, which is of lower polarity.
The place at which this transfer occurs is illustrated in Figure 8.19 as a thin circle
on the lower chromatographic plate. Because the overpressure is uniform throughout
the whole system, the compounds will be divided into two parts and migrate in both
circular (outwards) and ‘anticircular’ (inwords) directions. A hole at the centre of the
Figure 8.19 Schematic diagram of the combination of multilayers (decreasing polarity) for
OPLC with different types of development (circular and ‘anticircular’) and modes of
detection (off-line and on-line).