Page 47 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 47
24 New Trends in Eco-efficient and Recycled Concrete
Renewable energy is obtained from never-ending natural sources, either because of
the huge amount of energy that they contain, or because they are rapidly regener-
ated by natural means. In its different forms, renewable energies are derived
directly from the sun, rain, biomass, wind, ocean tides and heat generated and
stored in the Earth (Mohtasham, 2015).
Among the renewable resources, biomass is defined as organic matter from dif-
ferent plants, agricultural, industrial and urban waste. It is characterised by its great
energy potential that can be used to produce thermal energy, electricity and biofuel
(for transport). This energy source shows important advantages, including its contri-
bution to the economic and social development of the countries and regions where
it is produced as well as the reduction of waste disposal and CO 2 emissions, among
other benefits (Herna ´ndez et al., 2018).
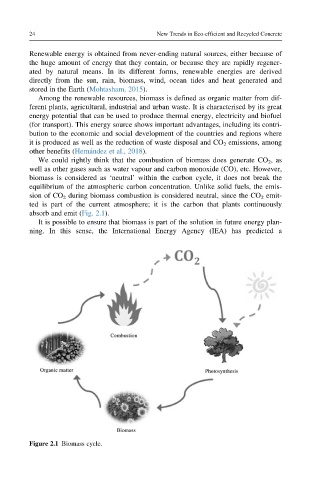
We could rightly think that the combustion of biomass does generate CO 2 ,as
well as other gases such as water vapour and carbon monoxide (CO), etc. However,
biomass is considered as ‘neutral’ within the carbon cycle, it does not break the
equilibrium of the atmospheric carbon concentration. Unlike solid fuels, the emis-
sion of CO 2 during biomass combustion is considered neutral, since the CO 2 emit-
ted is part of the current atmosphere; it is the carbon that plants continuously
absorb and emit (Fig. 2.1).
It is possible to ensure that biomass is part of the solution in future energy plan-
ning. In this sense, the International Energy Agency (IEA) has predicted a
Figure 2.1 Biomass cycle.