Page 514 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 514
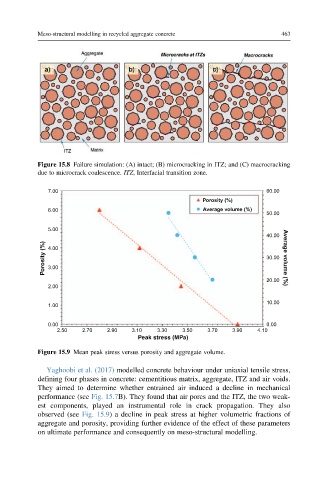
Meso-structural modelling in recycled aggregate concrete 463
Figure 15.8 Failure simulation: (A) intact; (B) microcracking in ITZ; and (C) macrocracking
due to microcrack coalescence. ITZ, Interfacial transition zone.
7.00 60.00
Porosity (%)
6.00 Average volume (%)
50.00
5.00
40.00
Porosity (%) 4.00 30.00 Average volume (%)
3.00
20.00
2.00
10.00
1.00
0.00 0.00
2.50 2.70 2.90 3.10 3.30 3.50 3.70 3.90 4.10
Peak stress (MPa)
Figure 15.9 Mean peak stress versus porosity and aggregate volume.
Yaghoobi et al. (2017) modelled concrete behaviour under uniaxial tensile stress,
defining four phases in concrete: cementitious matrix, aggregate, ITZ and air voids.
They aimed to determine whether entrained air induced a decline in mechanical
performance (see Fig. 15.7B). They found that air pores and the ITZ, the two weak-
est components, played an instrumental role in crack propagation. They also
observed (see Fig. 15.9) a decline in peak stress at higher volumetric fractions of
aggregate and porosity, providing further evidence of the effect of these parameters
on ultimate performance and consequently on meso-structural modelling.