Page 146 - Numerical Analysis and Modelling in Geomechanics
P. 146
STABILITY OF UNSATURATED SOIL SLOPES 127
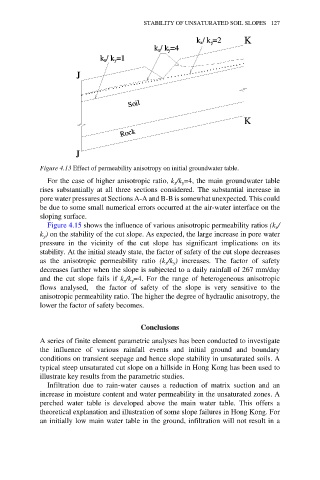
Figure 4.13 Effect of permeability anisotropy on initial groundwater table.
For the case of higher anisotropic ratio, k /k =4, the main groundwater table
x
y
rises substantially at all three sections considered. The substantial increase in
pore water pressures at Sections A-A and B-B is somewhat unexpected. This could
be due to some small numerical errors occurred at the air-water interface on the
sloping surface.
Figure 4.15 shows the influence of various anisotropic permeability ratios (k /
x
k ) on the stability of the cut slope. As expected, the large increase in pore water
y
pressure in the vicinity of the cut slope has significant implications on its
stability. At the initial steady state, the factor of safety of the cut slope decreases
as the anisotropic permeability ratio (k /k ) increases. The factor of safety
x
y
decreases further when the slope is subjected to a daily rainfall of 267 mm/day
and the cut slope fails if k /k =4. For the range of heterogeneous anisotropic
y
x
flows analysed, the factor of safety of the slope is very sensitive to the
anisotropic permeability ratio. The higher the degree of hydraulic anisotropy, the
lower the factor of safety becomes.
Conclusions
A series of finite element parametric analyses has been conducted to investigate
the influence of various rainfall events and initial ground and boundary
conditions on transient seepage and hence slope stability in unsaturated soils. A
typical steep unsaturated cut slope on a hillside in Hong Kong has been used to
illustrate key results from the parametric studies.
Infiltration due to rain-water causes a reduction of matrix suction and an
increase in moisture content and water permeability in the unsaturated zones. A
perched water table is developed above the main water table. This offers a
theoretical explanation and illustration of some slope failures in Hong Kong. For
an initially low main water table in the ground, infiltration will not result in a