Page 60 - Oil and Gas Production Handbook An Introduction to Oil and Gas Production
P. 60
5 Gas processing and LNG
Raw natural gas from the well consists of methane as well as many other
smaller fractions of heavier hydrocarbons, and various other components.
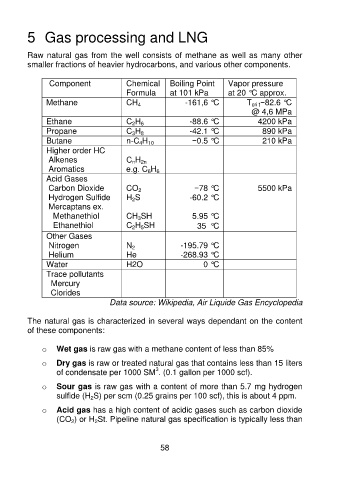
Component Chemical Boiling Point Vapor pressure
Formula at 101 kPa at 20 °C approx.
Methane CH 4 -161,6 °C T cri t−82.6 °C
@ 4,6 MPa
Ethane C 2H 6 -88.6 °C 4200 kPa
Propane C 3H 8 -42.1 °C 890 kPa
Butane n-C 4H 10 −0.5 °C 210 kPa
Higher order HC
Alkenes C nH 2n
Aromatics e.g. C 6H 6
Acid Gases
Carbon Dioxide CO 2 −78 °C 5500 kPa
Hydrogen Sulfide H 2S -60.2 °C
Mercaptans ex.
Methanethiol CH 3SH 5.95 °C
Ethanethiol C 2H 5SH 35 °C
Other Gases
Nitrogen N 2 -195.79 °C
Helium He -268.93 °C
Water H2O 0 °C
Trace pollutants
Mercury
Clorides
Data source: Wikipedia, Air Liquide Gas Encyclopedia
The natural gas is characterized in several ways dependant on the content
of these components:
o Wet gas is raw gas with a methane content of less than 85%
o Dry gas is raw or treated natural gas that contains less than 15 liters
3
of condensate per 1000 SM . (0.1 gallon per 1000 scf).
o Sour gas is raw gas with a content of more than 5.7 mg hydrogen
sulfide (H 2S) per scm (0.25 grains per 100 scf), this is about 4 ppm.
o Acid gas has a high content of acidic gases such as carbon dioxide
(CO 2) or H 2St. Pipeline natural gas specification is typically less than
58