Page 183 - Open-Hole Log Analysis and Formation Evaluation
P. 183
a
two
Original
This
Footal
shows
FIGURE
=
SP
—
referred
potential
measured
9.4
the
to
Ey
distinguish
so-called
can
+
—$+
t+
+
be
as
(see
the
may
total
components:
En,
the
.
SP
later
Conditions
=
liquid
membrane
include
SP.
measured
Current
LiquidJunction
Invaded
yet
in
under
picture.
SP.
Ea
It
the
junction
potential
Fe]
electrochemical
another
and
0
“Factors
(Z,,)
should
is
borehole
.
CC.
.
be
|=} V//
“eee: Current
by an
Affecting
Shale Y
noted
component,
created
Dynamic
components
the
of
the
that
(see
+3-
+3-
+}-
Sand
fe
the
electrode.
fig.
SP”),
ON Ne ——
SP.
9.5).
membrane potentials they
Figure
:
and
Conditions
the potential
When
are
electrokinetic
to
9.6
The
Ye
Water
Connate
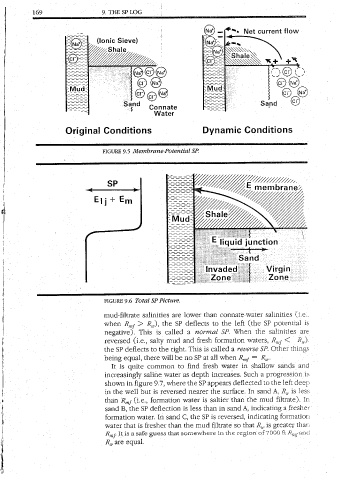
fe Fa] Zone - -=—=] ; + = Mud. : Filtrate -— a _ + ae ee — 9.3 Liquid-Junction Effects. FIGURE FIGURE cry Solution Solution Concentrated flow Net current 9. MEASUREMENTS OPEN-HOLE LOGGING Ll, 108
Original
in
R,,
the
Ryp
than
are
in
Rp
>
equal.
figure
R,),
9.7,
the
=
find
deflects
fresh
to
: vis a safe guess that somewhere in the region of 7000 ft Ry,pancl water that is fresher than the mud filtrate so that. 2, is greater thari formation water. In sand C, the SP is reversed, indicating formation sand B, the SP deflection is less than in sand A, indicating a fresher Ry Ci.e., formation water is saltier than the mud filtrate). In the well but is reversed n
SP.
called
the
a
water
liquid
Dynamic
left
in
When
LMU),
reverse
(the
the
SP.
to
SP
junction
the
:
Other
left
Conditions
eens
salinities
potential
is
deep