Page 269 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 269
Performance Impairments
Performance Impairments 259
Optical power
Front Back
dn dn
+ _
dt dt
_ _
2 1 0 1 2 t/t 0
d Frequency chirp
dt
+
_ _
2 1 0 1 2 t/t 0
_
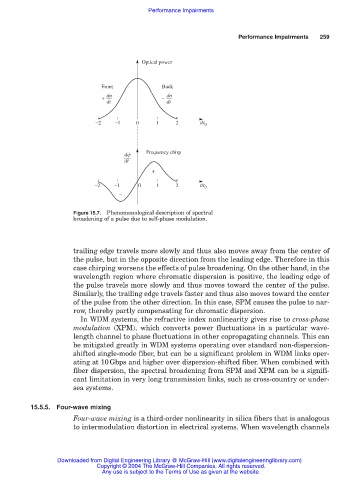
Figure 15.7. Phenomenological description of spectral
broadening of a pulse due to self-phase modulation.
trailing edge travels more slowly and thus also moves away from the center of
the pulse, but in the opposite direction from the leading edge. Therefore in this
case chirping worsens the effects of pulse broadening. On the other hand, in the
wavelength region where chromatic dispersion is positive, the leading edge of
the pulse travels more slowly and thus moves toward the center of the pulse.
Similarly, the trailing edge travels faster and thus also moves toward the center
of the pulse from the other direction. In this case, SPM causes the pulse to nar-
row, thereby partly compensating for chromatic dispersion.
In WDM systems, the refractive index nonlinearity gives rise to cross-phase
modulation (XPM), which converts power fluctuations in a particular wave-
length channel to phase fluctuations in other copropagating channels. This can
be mitigated greatly in WDM systems operating over standard non-dispersion-
shifted single-mode fiber, but can be a significant problem in WDM links oper-
ating at 10Gbps and higher over dispersion-shifted fiber. When combined with
fiber dispersion, the spectral broadening from SPM and XPM can be a signifi-
cant limitation in very long transmission links, such as cross-country or under-
sea systems.
15.5.5. Four-wave mixing
Four-wave mixing is a third-order nonlinearity in silica fibers that is analogous
to intermodulation distortion in electrical systems. When wavelength channels
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.