Page 327 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 327
Network Management
Network Management 317
Optical Optical Optical
mux amplifiers demux
Optical Optical
channels channels
Optical
OPM OPM OPM OPM
OPM
OPM
OPM
OPM
power
Control signals monitors
to transmitters
Supervisory channel
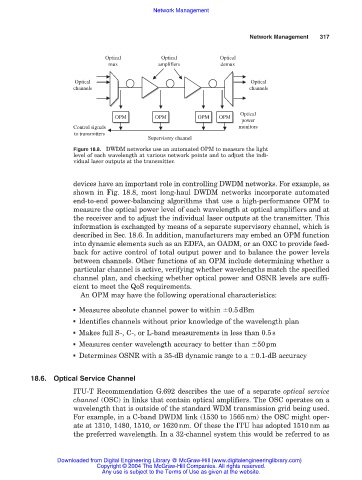
Figure 18.8. DWDM networks use an automated OPM to measure the light
level of each wavelength at various network points and to adjust the indi-
vidual laser outputs at the transmitter.
devices have an important role in controlling DWDM networks. For example, as
shown in Fig. 18.8, most long-haul DWDM networks incorporate automated
end-to-end power-balancing algorithms that use a high-performance OPM to
measure the optical power level of each wavelength at optical amplifiers and at
the receiver and to adjust the individual laser outputs at the transmitter. This
information is exchanged by means of a separate supervisory channel, which is
described in Sec. 18.6. In addition, manufacturers may embed an OPM function
into dynamic elements such as an EDFA, an OADM, or an OXC to provide feed-
back for active control of total output power and to balance the power levels
between channels. Other functions of an OPM include determining whether a
particular channel is active, verifying whether wavelengths match the specified
channel plan, and checking whether optical power and OSNR levels are suffi-
cient to meet the QoS requirements.
An OPM may have the following operational characteristics:
■ Measures absolute channel power to within 0.5dBm
■ Identifies channels without prior knowledge of the wavelength plan
■ Makes full S-, C-, or L-band measurements in less than 0.5s
■ Measures center wavelength accuracy to better than 50pm
■ Determines OSNR with a 35-dB dynamic range to a 0.1-dB accuracy
18.6. Optical Service Channel
ITU-T Recommendation G.692 describes the use of a separate optical service
channel (OSC) in links that contain optical amplifiers. The OSC operates on a
wavelength that is outside of the standard WDM transmission grid being used.
For example, in a C-band DWDM link (1530 to 1565nm) the OSC might oper-
ate at 1310, 1480, 1510, or 1620nm. Of these the ITU has adopted 1510nm as
the preferred wavelength. In a 32-channel system this would be referred to as
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.