Page 22 - Optical Switching And Networking Handbook
P. 22
Introduction to Optical Communications 7
fiber. Imagine two people talking on the phone at the same time, one
with a deep male voice and the other with a high-pitched female
voice. You can focus on one person or the other by listening for the
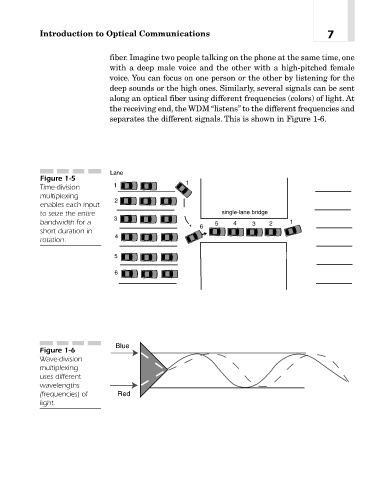
deep sounds or the high ones. Similarly, several signals can be sent
along an optical fiber using different frequencies (colors) of light. At
the receiving end, the WDM “listens” to the different frequencies and
separates the different signals. This is shown in Figure 1-6.
Lane
Figure 1-5 1
Time-division 1
multiplexing
2
enables each input
to seize the entire single-lane bridge
3
bandwidth for a 5 4 3 2 1
6
short duration in
4
rotation.
5
6
Blue
Figure 1-6
Wave-division
multiplexing
uses different
wavelengths
(frequencies) of Red
light.