Page 247 - Origin and Prediction of Abnormal Formation Pressures
P. 247
PREDICTION OF ABNORMALLY HIGH PRESSURES IN PETROLIFEROUS SALT-BEARING SECTIONS 219
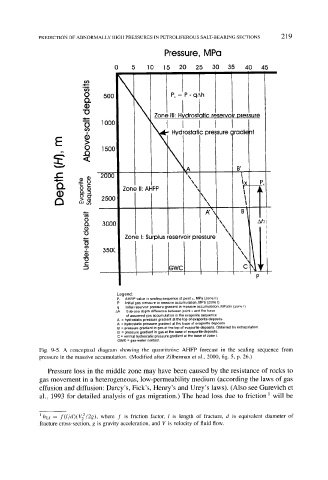
Pressure, MPa
0 5 ] 0 ] 5 20 25 30 35 40 45
[,, I i
0 500 Px = P - qAh
G)
t' reservoir pressure
Zone III ' H'/drosta ~c
000 \ i I ! I '
~ Hydrostatic pre~;sure ~radient
r
E >
O 500 , ,~,~ ~,A
:t: <
, __ , , B', ,
000 -- \ I
-,- 0 i \ ~x Px
Q. "ga 9 Zone I1" AHFP ~ \ --' ~k
s ~g !500 , ~ x ,,1 ~
o
D. 3000 / h
"o
Zone I: Surplus reservoir pressure \'~ \ ~ I
12I
!
"o
c Gwc , c \,~T
' I I ' I ! , P
Legend:
Px AHRP value in sealing sequence at point x, MPa (zone II)
P Initial gas pressure in massive accumulation, MPa (zone I)
q Initial reservoir pressure gradient in massive accumulation, MPa/m (zone I)
Ah Sub-sea depth difference between point x and the base
of assumed gas accumulation in the evaporite sequence
A = hydrostatic pressure gradient at the top of evaporite deposits.
A ~ = hydrostatic pressure gradient at the base of evaporite deposits.
B' = pressure gradient in gas at the top of evaporite deposits. Obtained by extrapolation.
B = pressure gradient in gas at the base of evaporite deposits.
C = normal hydrostatic pressure gradient at the base of zone I.
GWC = gas-water contact.
Fig. 9-5. A conceptual diagram showing the quantitative AHFP forecast in the sealing sequence from
pressure in the massive accumulation. (Modified after Zilberman et al., 2000, fig. 5, p. 26.)
Pressure loss in the middle zone may have been caused by the resistance of rocks to
gas movement in a heterogeneous, low-permeability medium (according the laws of gas
effusion and diffusion: Darcy's, Fick's, Henry's and Urey's laws). (Also see Gurevich et
al., 1993 for detailed analysis of gas migration.) The head loss due to friction 1 will be
l hLf = f(1/d)(Vf/2g), where f is friction factor, 1 is length of fracture, d is equivalent diameter of
fracture cross-section, g is gravity acceleration, and V is velocity of fluid flow.