Page 55 - PDA Robotics Using Your Personal Digital Assistant to Control Your Robot
P. 55
PDA 04 5/27/03 8:27 AM Page 31
Chapter 4 / Infrared Communications Overview
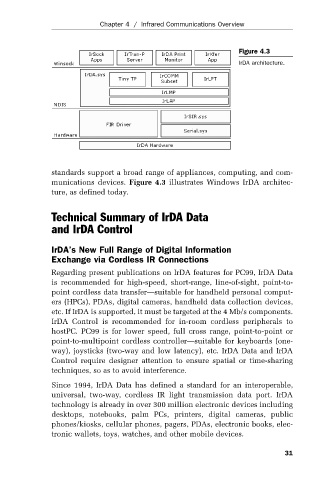
Figure 4.3
IrDA architecture.
standards support a broad range of appliances, computing, and com-
munications devices. Figure 4.3 illustrates Windows IrDA architec-
ture, as defined today.
Technical Summary of IrDA Data
and IrDA Control
IrDA’s New Full Range of Digital Information
Exchange via Cordless IR Connections
Regarding present publications on IrDA features for PC99, IrDA Data
is recommended for high-speed, short-range, line-of-sight, point-to-
point cordless data transfer—suitable for handheld personal comput-
ers (HPCs), PDAs, digital cameras, handheld data collection devices,
etc. If IrDA is supported, it must be targeted at the 4 Mb/s components.
IrDA Control is recommended for in-room cordless peripherals to
hostPC. PC99 is for lower speed, full cross range, point-to-point or
point-to-multipoint cordless controller—suitable for keyboards (one-
way), joysticks (two-way and low latency), etc. IrDA Data and IrDA
Control require designer attention to ensure spatial or time-sharing
techniques, so as to avoid interference.
Since 1994, IrDA Data has defined a standard for an interoperable,
universal, two-way, cordless IR light transmission data port. IrDA
technology is already in over 300 million electronic devices including
desktops, notebooks, palm PCs, printers, digital cameras, public
phones/kiosks, cellular phones, pagers, PDAs, electronic books, elec-
tronic wallets, toys, watches, and other mobile devices.
31