Page 113 - PVT Property Correlations
P. 113
Gas Condensates Chapter | 5 91
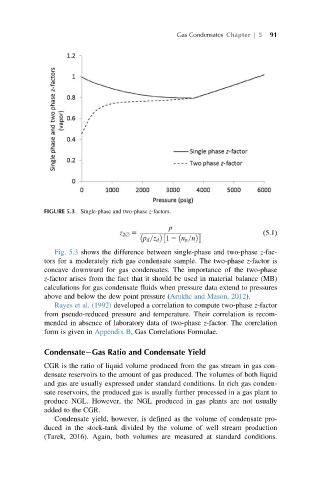
FIGURE 5.3 Single-phase and two-phase z-factors.
p
ð5:1Þ
z 2[ 5
p d =z d 1 2 n p =n
Fig. 5.3 shows the difference between single-phase and two-phase z-fac-
tors for a moderately rich gas condensate sample. The two-phase z-factor is
concave downward for gas condensates. The importance of the two-phase
z-factor arises from the fact that it should be used in material balance (MB)
calculations for gas condensate fluids when pressure data extend to pressures
above and below the dew point pressure (Arukhe and Mason, 2012).
Rayes et al. (1992) developed a correlation to compute two-phase z-factor
from pseudo-reduced pressure and temperature. Their correlation is recom-
mended in absence of laboratory data of two-phase z-factor. The correlation
form is given in Appendix B, Gas Correlations Formulae.
Condensate Gas Ratio and Condensate Yield
CGR is the ratio of liquid volume produced from the gas stream in gas con-
densate reservoirs to the amount of gas produced. The volumes of both liquid
and gas are usually expressed under standard conditions. In rich gas conden-
sate reservoirs, the produced gas is usually further processed in a gas plant to
produce NGL. However, the NGL produced in gas plants are not usually
added to the CGR.
Condensate yield, however, is defined as the volume of condensate pro-
duced in the stock-tank divided by the volume of well stream production
(Tarek, 2016). Again, both volumes are measured at standard conditions.