Page 120 - PVT Property Correlations
P. 120
98 PVT Property Correlations
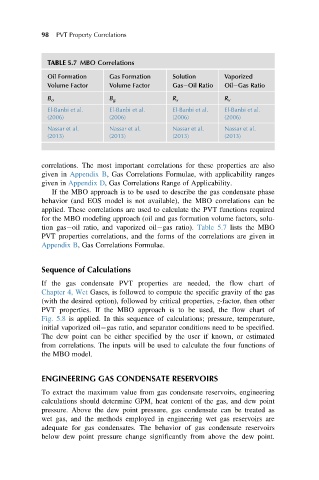
TABLE 5.7 MBO Correlations
Oil Formation Gas Formation Solution Vaporized
Volume Factor Volume Factor Gas Oil Ratio Oil Gas Ratio
B o
El-Banbi et al.
El-Banbi et al. B g R s R v
El-Banbi et al.
El-Banbi et al.
(2006) (2006) (2006) (2006)
Nassar et al. Nassar et al. Nassar et al. Nassar et al.
(2013) (2013) (2013) (2013)
correlations. The most important correlations for these properties are also
given in Appendix B, Gas Correlations Formulae, with applicability ranges
given in Appendix D, Gas Correlations Range of Applicability.
If the MBO approach is to be used to describe the gas condensate phase
behavior (and EOS model is not available), the MBO correlations can be
applied. These correlations are used to calculate the PVT functions required
for the MBO modeling approach (oil and gas formation volume factors, solu-
tion gas oil ratio, and vaporized oil gas ratio). Table 5.7 lists the MBO
PVT properties correlations, and the forms of the correlations are given in
Appendix B, Gas Correlations Formulae.
Sequence of Calculations
If the gas condensate PVT properties are needed, the flow chart of
Chapter 4, Wet Gases, is followed to compute the specific gravity of the gas
(with the desired option), followed by critical properties, z-factor, then other
PVT properties. If the MBO approach is to be used, the flow chart of
Fig. 5.8 is applied. In this sequence of calculations; pressure, temperature,
initial vaporized oil gas ratio, and separator conditions need to be specified.
The dew point can be either specified by the user if known, or estimated
from correlations. The inputs will be used to calculate the four functions of
the MBO model.
ENGINEERING GAS CONDENSATE RESERVOIRS
To extract the maximum value from gas condensate reservoirs, engineering
calculations should determine GPM, heat content of the gas, and dew point
pressure. Above the dew point pressure, gas condensate can be treated as
wet gas, and the methods employed in engineering wet gas reservoirs are
adequate for gas condensates. The behavior of gas condensate reservoirs
below dew point pressure change significantly from above the dew point.