Page 81 - PVT Property Correlations
P. 81
Dry Gases Chapter | 3 59
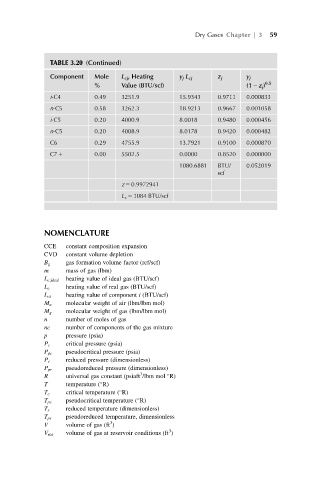
TABLE 3.20 (Continued)
Component Mole L cj , Heating y j L cj z j y j
% Value (BTU/scf) (1 2 z j ) 0.5
i-C4 0.49 3251.9 15.9343 0.9711 0.000833
n-C5 0.58 3262.3 18.9213 0.9667 0.001058
i-C5 0.20 4000.9 8.0018 0.9480 0.000456
n-C5 0.20 4008.9 8.0178 0.9420 0.000482
C6 0.29 4755.9 13.7921 0.9100 0.000870
C7 1 0.00 5502.5 0.0000 0.8520 0.000000
1080.6881 BTU/ 0.052019
scf
z 5 0.9972941
L c 5 1084 BTU/scf
NOMENCLATURE
CCE constant composition expansion
CVD constant volume depletion
B g gas formation volume factor (rcf/scf)
m mass of gas (lbm)
L c;ideal heating value of ideal gas (BTU/scf)
L c heating value of real gas (BTU/scf)
L ci heating value of component i (BTU/scf)
M a molecular weight of air (lbm/lbm mol)
M g molecular weight of gas (lbm/lbm mol)
n number of moles of gas
nc number of components of the gas mixture
p pressure (psia)
P c critical pressure (psia)
P pc pseudocritical pressure (psia)
reduced pressure (dimensionless)
P r
pseudoreduced pressure (dimensionless)
P pr
3
R universal gas constant (psiaft /lbm mol R)
T temperature ( R)
critical temperature ( R)
T c
T pc pseudocritical temperature ( R)
T r reduced temperature (dimensionless)
T pr pseudoreduced temperature, dimensionless
3
V volume of gas (ft )
3
V res volume of gas at reservoir conditions (ft )