Page 19 - Packed bed columns for absorption, desorption, rectification and direct heat transfer
P. 19
14
Equation (25) describes the steady state conductive heat transfer
process in immovable medium.
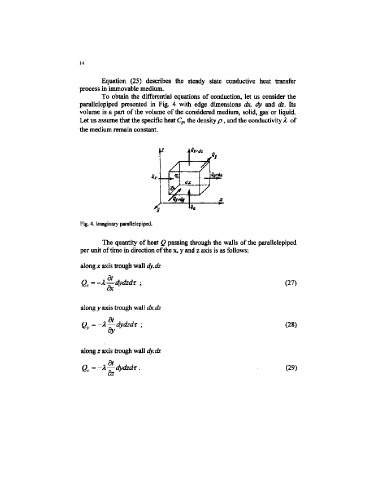
To obtain the differential equations of conduction, let us consider the
parallelepiped presented in Fig. 4 with edge dimensions dx, dy and dz. Its
volume is a part of the volume of the eonsidered medium, solid, gas or liquid.
Let us assume that the specific heat Cp, the density p, and the conductivity A, of
the medium remain constant.
Fig. 4. Imaginary parallelepiped.
The quantity of heat Q passing through the walls of the parallelepiped
per unit of time in direction of the x, y and z axis is as follows:
along x axis trough wall dy.dz
(27)
along y axis trough wall dx,dz
Q = -A—dythdr ; (28)
dy
along z axis trough wall dy.dz
Q = -X—dydzdt. (29)
dz