Page 196 - Automobile Mechanical and Electrical Systems Automotive Technology Vehicle Maintenance and Repair (Vehicle Maintenance Repr Nv2) by Tom Denton
P. 196
2
180 Automobile mechanical and electrical systems
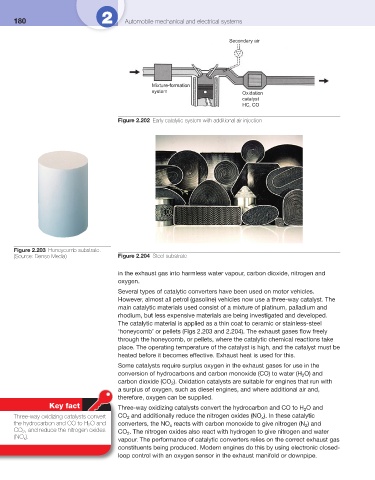
Secondary air
Mixture-formation
system Oxidation
catalyst
HC, CO
Figure 2.202 Early catalytic system with additional air injection
Figure 2.203 Honeycomb substrate.
(Source: Denso Media) Figure 2.204 Steel substrate
in the exhaust gas into harmless water vapour, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and
oxygen.
Several types of catalytic converters have been used on motor vehicles.
However, almost all petrol (gasoline) vehicles now use a three-way catalyst. The
main catalytic materials used consist of a mixture of platinum, palladium and
rhodium, but less expensive materials are being investigated and developed.
The catalytic material is applied as a thin coat to ceramic or stainless-steel
‘honeycomb’ or pellets ( Figs 2.203 and 2.204 ). The exhaust gases fl ow freely
through the honeycomb, or pellets, where the catalytic chemical reactions take
place. The operating temperature of the catalyst is high, and the catalyst must be
heated before it becomes effective. Exhaust heat is used for this.
Some catalysts require surplus oxygen in the exhaust gases for use in the
O) and
conversion of hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide (CO) to water (H 2
carbon dioxide (CO ). Oxidation catalysts are suitable for engines that run with
2
a surplus of oxygen, such as diesel engines, and where additional air and,
therefore, oxygen can be supplied.
Key fact Three-way oxidizing catalysts convert the hydrocarbon and CO to H 2 O and
Three-way oxidizing catalysts convert CO and additionally reduce the nitrogen oxides (NO ). In these catalytic
x
2
the hydrocarbon and CO to H 2 O and converters, the NO reacts with carbon monoxide to give nitrogen (N 2 ) and
x
CO 2 , and reduce the nitrogen oxides CO . The nitrogen oxides also react with hydrogen to give nitrogen and water
2
(NO x ).
vapour. The performance of catalytic converters relies on the correct exhaust gas
constituents being produced. Modern engines do this by using electronic closed-
loop control with an oxygen sensor in the exhaust manifold or downpipe.