Page 198 - Percolation Models for Transport in Porous Media With
P. 198
196 CHAPTER 11 GAS COLMATATION IN ELECTRIC ACTION
'f·"'·
0'----....U..---L--l
0
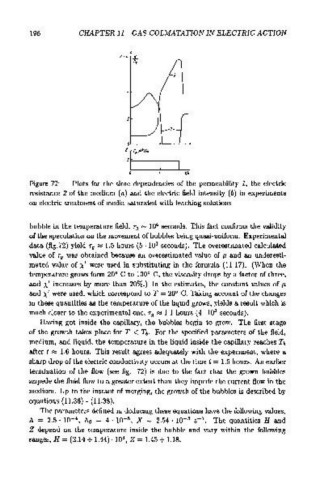
Figure 72: Plots for the time dependencies of the permeability 1, the electric
resistance 2 of the medium (a} and the electric field intensity {b) in experiments
on electric treatment of media saturated with leaching solutions
bubble in the temperature field, r 9 "' 10 4 seconds. This fact confirms the validity
of the speculation on the movement of bubbles being quasi-uniform. Experimental
data (fig.72} yield r 9 ~ 1.5 hours {5 · 10 3 seconds). The overestimated calculated
value of r 9 was obtained because an overestimated value of JL and an underesti-
mated value of x' were used in substituting in the formula {11.17}. (When the
temperature grows form 20° C to 100° C, the viscosity drops by a factor of three,
and x' increases by more than 20%.) In the estimates, the constant values of JL
and x' were used, which correspond to T = 20° C. Taking account of the changes
in these quantities as the temperature of the liquid grows, yields a result which is
much closer to the experimental one, r 9 ~ 1.1 hours (4 · 10 3 seconds).
Having got inside the capillary, the bubbles begin to grow. The first stage
of the growth takes place for T < Tb. For the specified parameters of the field,
medium, and liquid, the temperature in the liquid inside the capillary reaches n
after t ~ 1.6 hours. This result agrees adequately with the experiment, where a
sharp drop of the electric conductivity occurs at the time t = 1.5 hours. An earlier
termination of the flow (see fig. 72) is due to the fact that the grown bubbles
impede the fluid flow to a greater extent than they impede the current flow in the
medium. Up to the instant of merging, the growth of the bubbles is described by
equations (11.36)- (11.38).
The parameters defined in deducing these equations have the following values,
A = 2.5 · 10- , Ao = 4 · 10- 5 , X = 2.54 · 10- 5 s- 1 • The quantities H and
4
Z depend on the temperature inside the bubble and vary within the following
ranges, H = (2.14 + 1.44} · 10 3 , Z = 1.45 + 1.18.