Page 143 - Petroleum Geology
P. 143
120
( I
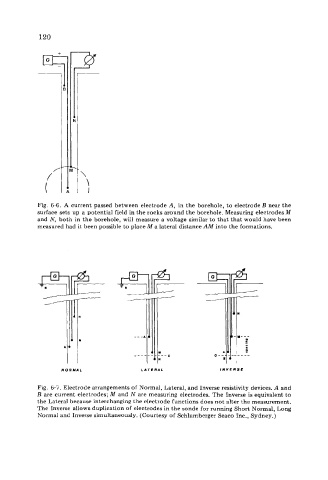
Fig. 6-6. A current passed between electrode A, in the borehole, to electrode B near the
surface sets up a potential field in the rocks around the borehole. Measuring electrodes M
and N, both in the borehole, will measure a voltage similar to that that would have been
measured had it been possible to place M a lateral distance AM into the formations.
I !
NORMAL LATERAL INVERSE
Fig. 6-7. Electrode arrangements of Normal, Lateral, and Inverse resistivity devices. A and
B are current electrodes; M and N are measuring electrodes. The Inverse is equivalent to
the Lateral because interchanging the electrode functions does not alter the measurement.
The Inverse allows duplication of electrodes in the sonde for running Short Normal, Long
Normal and Inverse simultaneously. (Courtesy of Schlumberger Seaco Inc., Sydney.)