Page 61 - Petroleum and Gas Field Processing
P. 61
2.2.1 Chemical Approach
Nearly all petroleum deposits are made up of a mixture of chemical
compounds that consist of hydrogen and carbon, known as hydrocarbons,
with varying amounts of nonhydrocarbons containing S, N 2 ,O 2 , and other
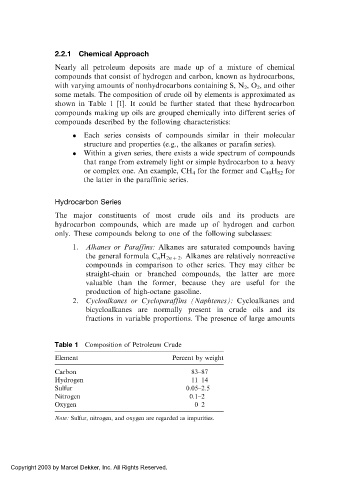
some metals. The composition of crude oil by elements is approximated as
shown in Table 1 [1]. It could be further stated that these hydrocarbon
compounds making up oils are grouped chemically into different series of
compounds described by the following characteristics:
Each series consists of compounds similar in their molecular
structure and properties (e.g., the alkanes or parafin series).
Within a given series, there exists a wide spectrum of compounds
that range from extremely light or simple hydrocarbon to a heavy
or complex one. An example, CH 4 for the former and C 40 H 82 for
the latter in the paraffinic series.
Hydrocarbon Series
The major constituents of most crude oils and its products are
hydrocarbon compounds, which are made up of hydrogen and carbon
only. These compounds belong to one of the following subclasses:
1. Alkanes or Paraffins: Alkanes are saturated compounds having
the general formula C n H 2n þ 2 . Alkanes are relatively nonreactive
compounds in comparison to other series. They may either be
straight-chain or branched compounds, the latter are more
valuable than the former, because they are useful for the
production of high-octane gasoline.
2. Cycloalkanes or Cycloparaffins (Naphtenes): Cycloalkanes and
bicycloalkanes are normally present in crude oils and its
fractions in variable proportions. The presence of large amounts
Table 1 Composition of Petroleum Crude
Element Percent by weight
Carbon 83–87
Hydrogen 11–14
Sulfur 0.05–2.5
Nitrogen 0.1–2
Oxygen 0–2
Note: Sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen are regarded as impurities.
Copyright 2003 by Marcel Dekker, Inc. All Rights Reserved.