Page 181 - Petrophysics
P. 181
154 PETROPHYSICS: RESERVOIR ROCK PROPERTIES
0.01
0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000 loo00
Horizontal permeablllty, mD
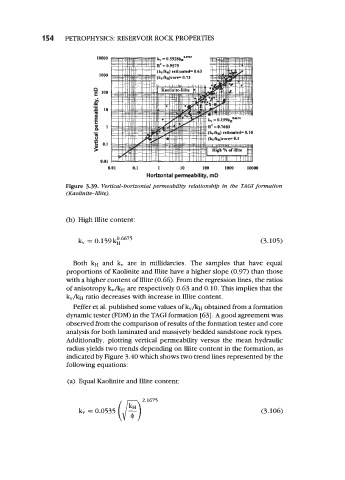
Figure 3.39. Verttcal-horlzontal permeability relationship in the TAGI formation
(Kaolinite-Illite).
(b) High Illite content:
0
kv = 0.159ki 6675 (3.105)
Both kH and kv are in millidarcies. The samples that have equal
proportions of Kaolinite and Illite have a higher slope (0.97) than those
with a higher content of Illite (0.66). From the regression lines, the ratios
of anisotropy kv/kH are respectively 0.63 and 0.10. This implies that the
kv/kH ratio decreases with increase in Illite content.
Peffer et al. published some values of kv/kH obtained from a formation
dynamic tester (FDM) in the TAGI formation [63]. A good agreement was
observed from the comparison of results of the formation tester and core
analysis for both laminated and massively bedded sandstone rock types.
Additionally, plotting vertical permeability versus the mean hydraulic
radius yields two trends depending on Illite content in the formation, as
indicated by Figure 3.40 which shows two trend lines represented by the
following equations:
(a) Equal Kaolinite and Illite content:
kv = 0.0535 (E) (3.106)
2.1675