Page 44 - Petrophysics
P. 44
18 PETROPHYSICS: RESERVOIR ROCK PROPERTIES
- -
20-- -
c
- -
io--
-
0. 1
I
SILT
SAND
MEDIUM I COARSE I V. FINE I FINE I MEDIUM I COARSE
PHI SCALE
6 5 4 3 2 0
01 I I I I
I I
1 164 1 /32 1116 1 I8 1 I4 112 1
Grain Size, mm
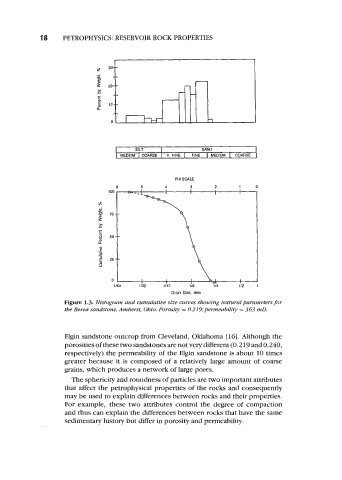
Figure 1.3. Histogram and cumulative size curves showing textural parametersfor
the Berea sandstone, Amherst, Ohio. Porosity = 0.219;permeability = 363 mD.
Elgin sandstone outcrop from Cleveland, Oklahoma [ 161. Although the
porosities of these two sandstones are not very different (0.219 and 0.240,
respectively) the permeability of the Elgin sandstone is about 10 times
greater because it is composed of a relatively large amount of coarse
grains, which produces a network of large pores.
The sphericity and roundness of particles are two important attributes
that affect the petrophysical properties of the rocks and consequently
may be used to explain differences between rocks and their properties.
For example, these two attributes control the degree of compaction
and thus can explain the differences between rocks that have the same
sedimentary history but differ in porosity and permeability.