Page 529 - Petrophysics
P. 529
INDICATORS OF NATURAL FRACTURES 497
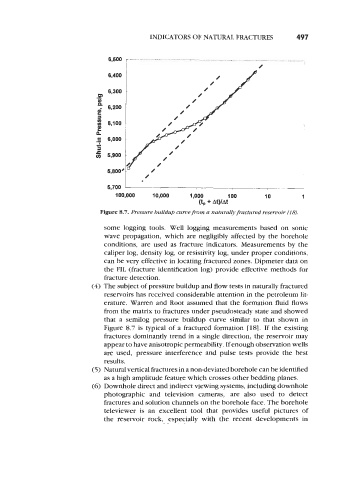
Figure 8.7. Pressure buildup curve from a naturally fractured reservoir [I SJ,
some logging tools. Well logging measurements based on sonic
wave propagation, which are negligibly affected by the borehole
conditions, are used as fracture indicators. Measurements by the
caliper log, density log, or resistivity log, under proper conditions,
can be very effective in locating fractured zones. Dipmeter data on
the FIL (fracture identification log) provide effective methods for
fracture detection.
(4) The subject of pressure buildup and flow tests in naturally fractured
reservoirs has received considerable attention in the petroleum lit-
erature. Warren and Root assumed that the formation fluid flows
from the matrix to fractures under pseudosteady state and showed
that a semilog pressure buildup curve similar to that shown in
Figure 8.7 is typical of a fractured formation [18]. If the existing
fractures dominantly trend in a single direction, the reservoir may
appear to have anisotropic permeability. If enough observation wells
are used, pressure interference and pulse tests provide the best
results.
(5) Natural vertical fractures in a non-deviated borehole can be identified
as a high amplitude feature which crosses other bedding planes.
(6) Downhole direct and indirect viewing systems, including downhole
photographic and television cameras, are also used to detect
fractures and solution channels on the borehole face. The borehole
televiewer is an excellent tool that provides useful pictures of
the reservoir rock, especially with the recent developments in