Page 139 - Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
P. 139
126 Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
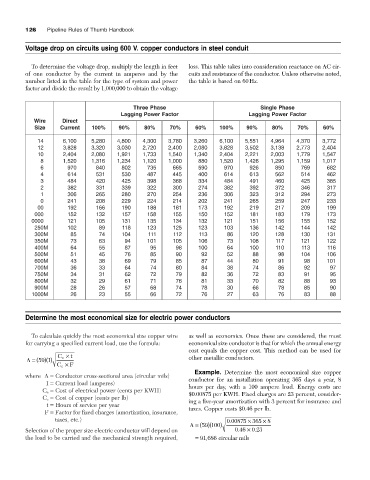
Voltage drop on circuits using 600 V. copper conductors in steel conduit
To determine the voltage drop, multiply the length in feet loss. This table takes into consideration reactance on AC cir-
of one conductor by the current in amperes and by the cuits and resistance of the conductor. Unless otherwise noted,
number listed in the table for the type of system and power the table is based on 60Hz.
factor and divide the result by 1,000,000 to obtain the voltage
Three Phase Single Phase
Lagging Power Factor Lagging Power Factor
Wire Direct
Size Current 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 100% 90% 80% 70% 60%
14 6,100 5,280 4,800 4,300 3,780 3,260 6,100 5,551 4,964 4,370 3,772
12 3,828 3,320 3,030 2,720 2,400 2,080 3,828 3,502 3,138 2,773 2,404
10 2,404 2,080 1,921 1,733 1,540 1,340 2,404 2,221 2,003 1,779 1,547
8 1,520 1,316 1,234 1,120 1,000 880 1,520 1,426 1,295 1,159 1,017
6 970 840 802 735 665 590 970 926 850 769 682
4 614 531 530 487 445 400 614 613 562 514 462
3 484 420 425 398 368 334 484 491 460 425 385
2 382 331 339 322 300 274 382 392 372 346 317
1 306 265 280 270 254 236 306 323 312 294 273
0 241 208 229 224 214 202 241 265 259 247 233
00 192 166 190 188 181 173 192 219 217 209 199
000 152 132 157 158 155 150 152 181 183 179 173
0000 121 105 131 135 134 132 121 151 156 155 152
250M 102 89 118 123 125 123 103 136 142 144 142
300M 85 74 104 111 112 113 86 120 128 130 131
350M 73 63 94 101 105 106 73 108 117 121 122
400M 64 55 87 95 98 100 64 100 110 113 116
500M 51 45 76 85 90 92 52 88 98 104 106
600M 43 38 69 79 85 87 44 80 91 98 101
700M 36 33 64 74 80 84 38 74 86 92 97
750M 34 31 62 72 79 82 36 72 83 91 95
800M 32 29 61 71 76 81 33 70 82 88 93
900M 28 26 57 68 74 78 30 66 78 85 90
1000M 26 23 55 66 72 76 27 63 76 83 88
Determine the most economical size for electric power conductors
To calculate quickly the most economical size copper wire as well as economics. Once these are considered, the most
for carrying a specified current load, use the formula: economical size conductor is that for which the annual energy
cost equals the copper cost. This method can be used for
C e ¥ t
A = ()( I) other metallic conductors.
59
C c ¥ F
Example. Determine the most economical size copper
where A = Conductor cross-sectional area (circular mils)
conductor for an installation operating 365 days a year, 8
I = Current load (amperes)
hours per day, with a 100 ampere load. Energy costs are
C e = Cost of electrical power (cents per KWH)
$0.00875 per KWH. Fixed charges are 23 percent, consider-
C c = Cost of copper (cents per lb)
ing a five-year amortization with 3 percent for insurance and
t = Hours of service per year
taxes. Copper costs $0.46 per lb.
F = Factor for fixed charges (amortization, insurance,
taxes, etc.) 0 00875 ¥ 365 ¥ 8
.
59
A = ()(100 )
.
.
Selection of the proper size electric conductor will depend on 046 ¥ 0 23
,
the load to be carried and the mechanical strength required, = 91 686 circular mils