Page 39 - Plant-Based Remediation Processes
P. 39
26 M. Barbafieri et al.
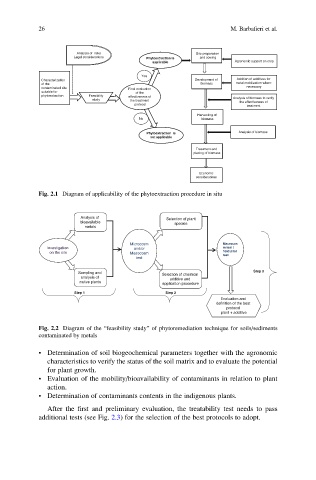
Analysis of risks Site preparation
Legal considerations Phytoextraction is and sowing
applicable Agronomic support on crop
Yes
Characterization Development of Addition of additives for
of the biomass metal mobilization where
contaminated site Final evaluation necessary
suitable for of the
phytoextraction Feasibility effectiveness of
study the treatment Analysis of biomass to verify
the effectiveness of
protocol
treatment
Harvesting of
No biomass
Phytoextraction is Analysis of biomass
not applicable
Treatment and
placing of biomass
Economic
considerations
Fig. 2.1 Diagram of applicability of the phytoextraction procedure in situ
Analysis of
Selection of plant
bioavailable species
metals
Microcosm Macrocos
Investigation and/or m test /
on the site Mesocosm field pilot
test
test
Sampling and Step 3
Selection of chemical
analysis of additive and
native plants application procedure
Step 1 Step 2
Evaluation and
definition of the best
protocol
plant + additive
Fig. 2.2 Diagram of the “feasibility study” of phytoremediation technique for soils/sediments
contaminated by metals
• Determination of soil biogeochemical parameters together with the agronomic
characteristics to verify the status of the soil matrix and to evaluate the potential
for plant growth.
• Evaluation of the mobility/bioavailability of contaminants in relation to plant
action.
• Determination of contaminants contents in the indigenous plants.
After the first and preliminary evaluation, the treatability test needs to pass
additional tests (see Fig. 2.3) for the selection of the best protocols to adopt.