Page 231 - Plastics Engineering
P. 231
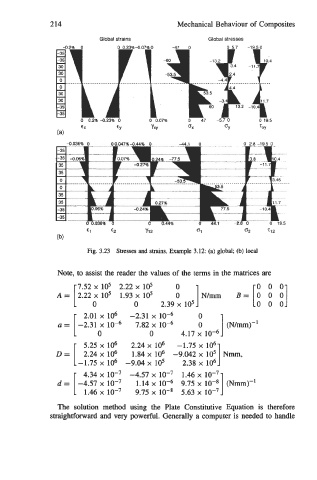
214 Mechanical Behaviour of Composites
Global strains Global stresses
4.2% 0 0 0.23% 4 07% 0 -47 0 0 57 -19.50
0 02%423% 0 0 0.07% 0 47 -57 0 0 19.5
.. ._ ...... .....
. . _ ........................
........ .....
€1 €2 'y12 01 02 712
(b)
Fig. 3.23 Stresses and strains, Example 3.12: (a) global; (b) local
Note, to assist the reader the values of the terms in the matrices are
A = 2.22 x 105 1.93 x 16 x 000
17.52; 105 2.22 x 105
[o 0 01
0 2.39 x 105 IN/- B= 0 0 0
[ 2.01; lo6 -2.31 x
u = -2.31 x 7.82 x 0 ] (N/mm)-'
0 4.17 x
D= [ 5.25 x lo6 2.24 x lo6 -1.75 x lo6
2.38 x lo6 1
1.84 x lo6 -9.042 x lo5 Nmm,
2.24 x lo6
-1.75 x lo6 -9.04 x 16
4.34 x 10-~ -4.57 x 10-~ 1.46 x 10-~
-4.57 x 1.14 x 9.75 x 1 (NIIMI)-'
1.46 x 10-~ 9.75 x io-8 5.63 x 10-~
The solution method using the Plate Constitutive Equation is therefore
straightforward and very powerful. Generally a computer is needed to handle