Page 256 - Plastics Engineering
P. 256
Mechanical Behaviour of Composites 239
120
20
0
10’ 1 0’ 103 104 105 1 06 1 07
Cycles to fracture
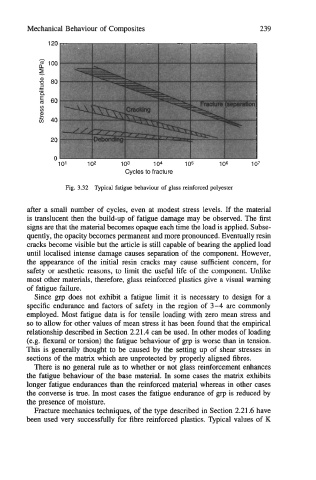
Fig. 3.32 1s.pical fatigue behaviour of glass reinforced polyester
after a small number of cycles, even at modest stress levels. If the material
is translucent then the build-up of fatigue damage may be observed. The first
signs are that the material becomes opaque each time the load is applied. Subse-
quently, the opacity becomes permanent and more pronounced. Eventually resin
cracks become visible but the article is still capable of bearing the applied load
until localised intense damage causes separation of the component. However,
the appearance of the initial resin cracks may cause sufficient concern, for
safety or aesthetic reasons, to limit the useful life of the component. Unlike
most other materials, therefore, glass reinforced plastics give a visual warning
of fatigue failure.
Since grp does not exhibit a fatigue limit it is necessary to design for a
specific endurance and factors of safety in the region of 3-4 are commonly
employed. Most fatigue data is for tensile loading with zero mean stress and
so to allow for other values of mean stress it has been found that the empirical
relationship described in Section 2.21.4 can be used. In other modes of loading
(e.g. flexural or torsion) the fatigue behaviour of grp is worse than in tension.
This is generally thought to be caused by the setting up of shear stresses in
sections of the matrix which are unprotected by properly aligned fibres.
There is no general rule as to whether or not glass reinforcement enhances
the fatigue behaviour of the base material. In some cases the matrix exhibits
longer fatigue endurances than the reinforced material whereas in other cases
the converse is true. In most cases the fatigue endurance of grp is reduced by
the presence of moisture.
Fracture mechanics techniques, of the type described in Section 2.21.6 have
been used very successfully for fibre reinforced plastics. Qpical values of K