Page 697 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 697
640 Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
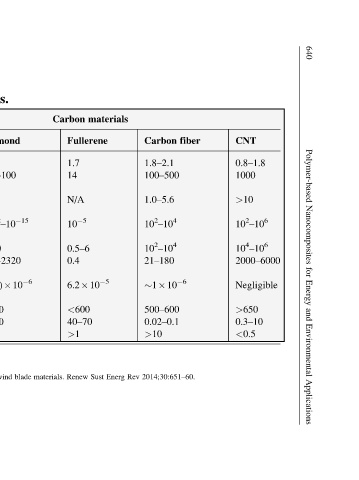
CNT 0.8–1.8 1000 >10 10 2 –10 6 10 4 –10 6 2000–6000 Negligible >650 0.3–10 <0.5
fiber
Carbon 1.8–2.1 100–500 1.0–5.6 10 2 –10 4 10 2 –10 4 21–180 1 10 6 500–600 0.02–0.1 >10 2014;30:651–60.
Rev
materials 6.2 10 5 Energ Sust
Carbon Fullerene 1.7 14 N/A 10 5 0.5–6 0.4 <600 40–70 >1 Renew
materials. blade
materials. Diamond 3.5 500–100 1.2 10 2 –10 15 1800 900–2320 (1–3) 10 6 <600 >100 >5 wind for nanocomposites
carbon-based Graphite 1.9–2.3 1000 a 36.5 b 10 a <0.01 b 4000 a 3.3 b 10 4 298 a 2.2 b 1 10 6a 2.9 10 –5b 450–600 0.01–0.002 >10 nanotubes/polymer
various (K 1 ) (wt%) carbon of
of (S/cm) s)) K)) (W/(m expansion (°C) matrix Perspectives
Properties (g/cm 3 ) (GPa) (GPa) conductivity (cm 2 /(V conductivity thermal air in (US$/g) polymer in Y. Zhang P-C,
24.1 gravity modulus strength mobility of stability content Ma of
Table Properties Specific Tensile Tensile Electric Electron Thermal Coefficient Thermal Cost/price General a In-plane. b c-axis. Courtesy