Page 708 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 708
Carbon nanotube-based nanocomposites for wind turbine applications 651
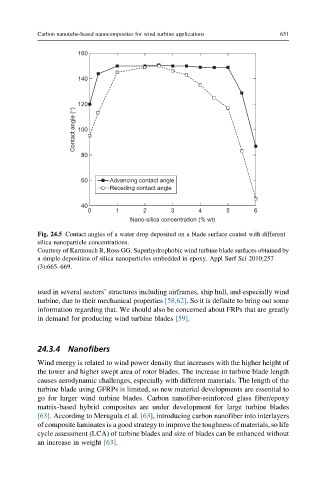
160
140
120
Contact angle (°) 100
80
60 Advancing contact angle
Receding contact angle
40
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Nano-silica concentration (% wt)
Fig. 24.5 Contact angles of a water drop deposited on a blade surface coated with different
silica nanoparticle concentrations.
Courtesy of Karmouch R, Ross GG. Superhydrophobic wind turbine blade surfaces obtained by
a simple deposition of silica nanoparticles embedded in epoxy. Appl Surf Sci 2010;257
(3):665–669.
used in several sectors’ structures including airframes, ship hull, and especially wind
turbine, due to their mechanical properties [58,62]. So it is definite to bring out some
information regarding that. We should also be concerned about FRPs that are greatly
in demand for producing wind turbine blades [59].
24.3.4 Nanofibers
Wind energy is related to wind power density that increases with the higher height of
the tower and higher swept area of rotor blades. The increase in turbine blade length
causes aerodynamic challenges, especially with different materials. The length of the
turbine blade using GFRPs is limited, so new material developments are essential to
go for larger wind turbine blades. Carbon nanofiber-reinforced glass fiber/epoxy
matrix-based hybrid composites are under development for large turbine blades
[63]. According to Merugula et al. [63], introducing carbon nanofiber into interlayers
of composite laminates is a good strategy to improve the toughness of materials, so life
cycle assessment (LCA) of turbine blades and size of blades can be enhanced without
an increase in weight [63].