Page 72 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 72
Preparation and properties of nanopolymer advanced composites: A review 49
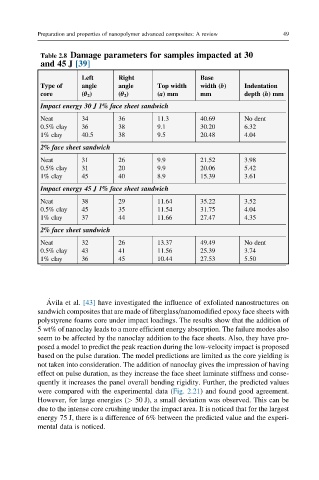
Table 2.8 Damage parameters for samples impacted at 30
and 45 J [39]
Left Right Base
Type of angle angle Top width width (b) Indentation
core (θ 2 ) (θ 2 ) (a)mm mm depth (h)mm
Impact energy 30 J 1% face sheet sandwich
Neat 34 36 11.3 40.69 No dent
0.5% clay 36 38 9.1 30.20 6.32
1% clay 40.5 38 9.5 20.48 4.04
2% face sheet sandwich
Neat 31 26 9.9 21.52 3.98
0.5% clay 31 20 9.9 20.06 5.42
1% clay 45 40 8.9 15.39 3.61
Impact energy 45 J 1% face sheet sandwich
Neat 38 29 11.64 35.22 3.52
0.5% clay 45 35 11.54 31.75 4.04
1% clay 37 44 11.66 27.47 4.35
2% face sheet sandwich
Neat 32 26 13.37 49.49 No dent
0.5% clay 43 41 11.56 25.39 3.74
1% clay 36 45 10.44 27.53 5.50
´
Avila et al. [43] have investigated the influence of exfoliated nanostructures on
sandwich composites that are made of fiberglass/nanomodified epoxy face sheets with
polystyrene foams core under impact loadings. The results show that the addition of
5 wt% of nanoclay leads to a more efficient energy absorption. The failure modes also
seem to be affected by the nanoclay addition to the face sheets. Also, they have pro-
posed a model to predict the peak reaction during the low-velocity impact is proposed
based on the pulse duration. The model predictions are limited as the core yielding is
not taken into consideration. The addition of nanoclay gives the impression of having
effect on pulse duration, as they increase the face sheet laminate stiffness and conse-
quently it increases the panel overall bending rigidity. Further, the predicted values
were compared with the experimental data (Fig. 2.21) and found good agreement.
However, for large energies (> 50 J), a small deviation was observed. This can be
due to the intense core crushing under the impact area. It is noticed that for the largest
energy 75 J, there is a difference of 6% between the predicted value and the experi-
mental data is noticed.