Page 16 - Primer on Enhanced Oil Recovery
P. 16
Hydrocarbon and oil reserves classification 7
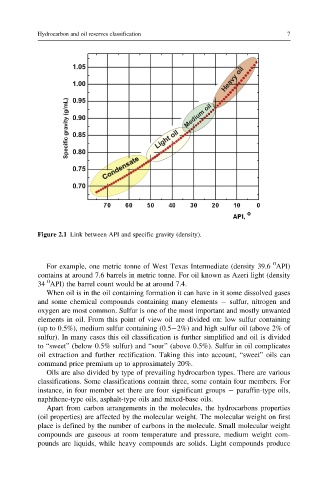
Figure 2.1 Link between API and specific gravity (density).
0
For example, one metric tonne of West Texas Intermediate (density 39.6 API)
contains at around 7.6 barrels in metric tonne. For oil known as Azeri light (density
0
34 API) the barrel count would be at around 7.4.
When oil is in the oil containing formation it can have in it some dissolved gases
and some chemical compounds containing many elements sulfur, nitrogen and
oxygen are most common. Sulfur is one of the most important and mostly unwanted
elements in oil. From this point of view oil are divided on: low sulfur containing
(up to 0.5%), medium sulfur containing (0.5 2%) and high sulfur oil (above 2% of
sulfur). In many cases this oil classification is further simplified and oil is divided
to “sweet” (below 0.5% sulfur) and “sour” (above 0.5%). Sulfur in oil complicates
oil extraction and further rectification. Taking this into account, “sweet” oils can
command price premium up to approximately 20%.
Oils are also divided by type of prevailing hydrocarbon types. There are various
classifications. Some classifications contain three, some contain four members. For
instance, in four member set there are four significant groups paraffin-type oils,
naphthene-type oils, asphalt-type oils and mixed-base oils.
Apart from carbon arrangements in the molecules, the hydrocarbons properties
(oil properties) are affected by the molecular weight. The molecular weight on first
place is defined by the number of carbons in the molecule. Small molecular weight
compounds are gaseous at room temperature and pressure, medium weight com-
pounds are liquids, while heavy compounds are solids. Light compounds produce