Page 40 - Principles of Catalyst Development
P. 40
Part I: Reservoir Engineering Primer 21
condition in a rock/fluid system depends on IFT. Changing the type of rock or
fluid can change IFT and, hence, wettability of the system. Adding a chemical
such as surfactant, polymer, corrosion inhibitor, or scale inhibitor can alter
wettability.
Contact Angle
Wettability is measured by contact angle. Contact angle is always
measured through the more dense phase. Contact angle is related to interfacial
energies by
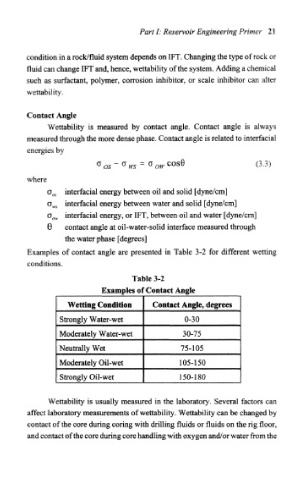
os ws a ow cos0 (3.3)
where
o os interfacial energy between oil and solid [dyne/cm]
interfacial energy between water and solid [dyne/cm]
o m
interfacial energy, or IFT, between oil and water [dyne/cm]
o ow
0 contact angle at oil-water-solid interface measured through
the water phase [degrees]
Examples of contact angle are presented in Table 3-2 for different wetting
conditions.
Table 3-2
Examples of Contact Angle
Wetting Condition Contact Angle, degrees
Strongly Water- wet 0-30
Moderately Water-wet 30-75
Neutrally Wet 75-105
Moderately Oil-wet 105-150
Strongly Oil-wet 150-180
Wettability is usually measured in the laboratory. Several factors can
affect laboratory measurements of wettability. Wettability can be changed by
contact of the core during coring with drilling fluids or fluids on the rig floor,
and contact of the core during core handling with oxygen and/or water from the