Page 181 - Process Equipment and Plant Design Principles and Practices by Subhabrata Ray Gargi Das
P. 181
6.4 Evaporator performance 179
Thermocompression ejector
Steam
I II III
Vapour to
vacuum
Feed Product
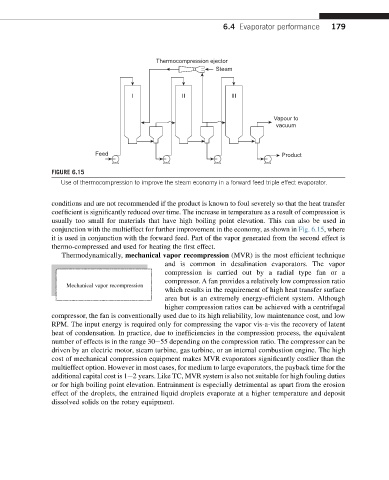
FIGURE 6.15
Use of thermocompression to improve the steam economy in a forward feed triple effect evaporator.
conditions and are not recommended if the product is known to foul severely so that the heat transfer
coefficient is significantly reduced over time. The increase in temperature as a result of compression is
usually too small for materials that have high boiling point elevation. This can also be used in
conjunction with the multieffect for further improvement in the economy, as shown in Fig. 6.15, where
it is used in conjunction with the forward feed. Part of the vapor generated from the second effect is
thermo-compressed and used for heating the first effect.
Thermodynamically, mechanical vapor recompression (MVR) is the most efficient technique
andiscommonindesalinationevaporators.The vapor
compression is carried out by a radial type fan or a
compressor. A fan provides a relatively low compression ratio
Mechanical vapor recompression
which results in the requirement of high heat transfer surface
area but is an extremely energy-efficient system. Although
higher compression ratios can be achieved with a centrifugal
compressor, the fan is conventionally used due to its high reliability, low maintenance cost, and low
RPM. The input energy is required only for compressing the vapor vis-a-vis the recovery of latent
heat of condensation. In practice, due to inefficiencies in the compression process, the equivalent
number of effects is in the range 30e55 depending on the compression ratio. The compressor can be
driven by an electric motor, steam turbine, gas turbine, or an internal combustion engine. The high
cost of mechanical compression equipment makes MVR evaporators significantly costlier than the
multieffect option. However in most cases, for medium to large evaporators, the payback time for the
additional capital cost is 1e2 years. Like TC, MVR system is also not suitable for high fouling duties
or for high boiling point elevation. Entrainment is especially detrimental as apart from the erosion
effect of the droplets, the entrained liquid droplets evaporate at a higher temperature and deposit
dissolved solids on the rotary equipment.