Page 118 -
P. 118
100 4 Getting the Data
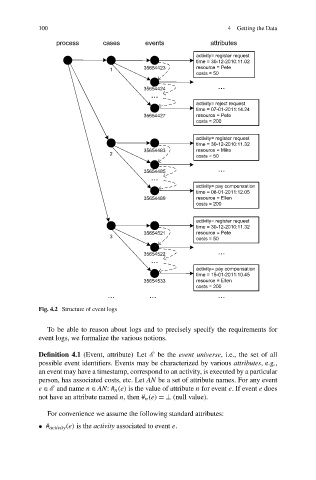
Fig. 4.2 Structure of event logs
To be able to reason about logs and to precisely specify the requirements for
event logs, we formalize the various notions.
Definition 4.1 (Event, attribute) Let E be the event universe, i.e., the set of all
possible event identifiers. Events may be characterized by various attributes, e.g.,
an event may have a timestamp, correspond to an activity, is executed by a particular
person, has associated costs, etc. Let AN be a set of attribute names. For any event
e ∈ E and name n ∈ AN:# n (e) is the value of attribute n for event e. If event e does
not have an attribute named n, then # n (e) =⊥ (null value).
For convenience we assume the following standard attributes:
• # activity (e) is the activity associated to event e.