Page 63 - Programming the Photon Getting Started With the Internet of Things
P. 63
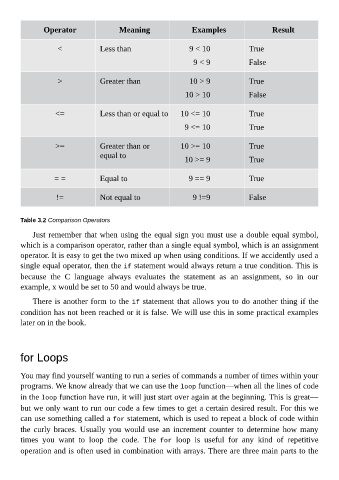
Operator Meaning Examples Result
< Less than 9 < 10 True
9 < 9 False
> Greater than 10 > 9 True
10 > 10 False
<= Less than or equal to 10 <= 10 True
9 <= 10 True
>= Greater than or 10 >= 10 True
equal to
10 >= 9 True
= = Equal to 9 == 9 True
!= Not equal to 9 !=9 False
Table 3.2 Comparison Operators
Just remember that when using the equal sign you must use a double equal symbol,
which is a comparison operator, rather than a single equal symbol, which is an assignment
operator. It is easy to get the two mixed up when using conditions. If we accidently used a
single equal operator, then the if statement would always return a true condition. This is
because the C language always evaluates the statement as an assignment, so in our
example, x would be set to 50 and would always be true.
There is another form to the if statement that allows you to do another thing if the
condition has not been reached or it is false. We will use this in some practical examples
later on in the book.
for Loops
You may find yourself wanting to run a series of commands a number of times within your
programs. We know already that we can use the loop function—when all the lines of code
in the loop function have run, it will just start over again at the beginning. This is great—
but we only want to run our code a few times to get a certain desired result. For this we
can use something called a for statement, which is used to repeat a block of code within
the curly braces. Usually you would use an increment counter to determine how many
times you want to loop the code. The for loop is useful for any kind of repetitive
operation and is often used in combination with arrays. There are three main parts to the