Page 75 - Programming the Raspberry Pi Getting Started with Python
P. 75
The key to understanding such layouts is the use of the sticky attributes of the components to
decide which walls of their grid cell they should stick to. To control which of the columns and rows
expand when the window is resized, you use the columnconfigure and rowconfigure commands.
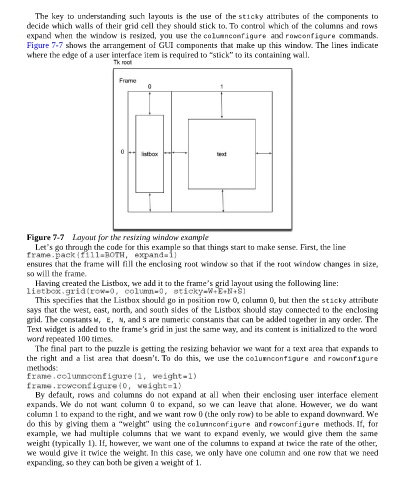
Figure 7-7 shows the arrangement of GUI components that make up this window. The lines indicate
where the edge of a user interface item is required to “stick” to its containing wall.
Figure 7-7 Layout for the resizing window example
Let’s go through the code for this example so that things start to make sense. First, the line
ensures that the frame will fill the enclosing root window so that if the root window changes in size,
so will the frame.
Having created the Listbox, we add it to the frame’s grid layout using the following line:
This specifies that the Listbox should go in position row 0, column 0, but then the sticky attribute
says that the west, east, north, and south sides of the Listbox should stay connected to the enclosing
grid. The constants W, E, N, and S are numeric constants that can be added together in any order. The
Text widget is added to the frame’s grid in just the same way, and its content is initialized to the word
word repeated 100 times.
The final part to the puzzle is getting the resizing behavior we want for a text area that expands to
the right and a list area that doesn’t. To do this, we use the columnconfigure and rowconfigure
methods:
By default, rows and columns do not expand at all when their enclosing user interface element
expands. We do not want column 0 to expand, so we can leave that alone. However, we do want
column 1 to expand to the right, and we want row 0 (the only row) to be able to expand downward. We
do this by giving them a “weight” using the columnconfigure and rowconfigure methods. If, for
example, we had multiple columns that we want to expand evenly, we would give them the same
weight (typically 1). If, however, we want one of the columns to expand at twice the rate of the other,
we would give it twice the weight. In this case, we only have one column and one row that we need
expanding, so they can both be given a weight of 1.