Page 13 - Radiochemistry and nuclear chemistry
P. 13
Radiochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry
assumption that these minerals contain elements which are more active than uranium". She
and her husband, Pierre Curie, began a careful purification of pitchblende, measuring the
amount of radiation in the solution and in the precipitate after each precipitation separation
step. These first radiochemical investigations were highly successful: "while carrying out
these operations, more active products are obtained. Finally, we obtained a substance whose
activity was 400 times larger than that of uranium. We therefore believe that the substance
that we have isolated from pitchblende is a hitherto unknown metal. If the existence of this
metal can be affirmed, we suggest the name polonium." It was in the publication reporting
the discovery of polonium in 1898 that the word radioactive was used for the first time. It
may be noted that the same element was simultaneously and independently discovered by
W. Marckwald who called it "radiotellurium".
In the same year the Curies, together with G. Bemont, isolated another radioactive
substance for which they suggested the name radium. In order to prove that polonium and
radium were in fact two new elements, large amounts of pitchblende were processed, and
in 1902 M. Curie announced that she had been able to isolate about 0.1 g of pure radium
chloride from more than one ton of pitchblende waste. The determination of the atomic
weight of radium and the measurement of its emission spectrum provided the final proof
that a new element had been isolated.
1.2. Radioactive decay
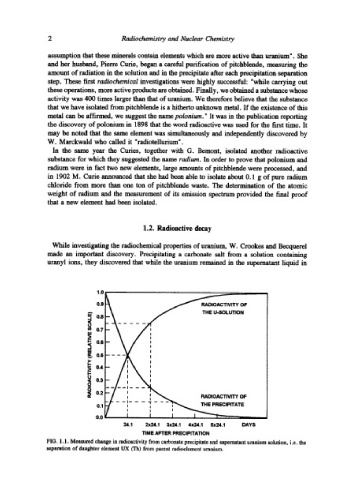
While investigating the radiochemical properties of uranium, W. Crookes and Becquerel
made an important discovery. Precipitating a carbonate salt from a solution containing
uranyl ions, they discovered that while the uranium remained in the supernatant liquid in
1.o
o.9 RADIOACTIVITY OF
THE U-SOLUTION
m 0.8
-I
0.7
UI
~ .6
~ 0.5
_~ o.4
u
F-
I~ 0.3
|m .,...., ~
_~ 0.2 l I
I l RADIOACTIVITY OF
I . . . . I" -- - THE PRECIPITATE
0.1 I i
l i
0.0
24.1 2x24.1 3x24.1 4x24.1 5x24.1 DAYS
TIME AFTER PRECIPITATION
FIG. 1.1. Measured change in radioactivity from carbonate precipitate and supematant uranium solution, i.e. the
separation of daughter element UX (Th) from parent radioelement uranium.