Page 81 - Refining Biomass Residues for Sustainable Energy and Bioproducts
P. 81
56 Refining Biomass Residues for Sustainable Energy and Bioproducts
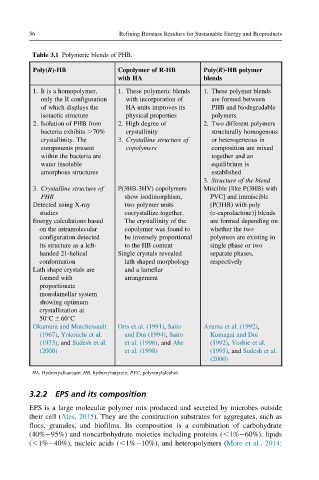
Table 3.1 Polymeric blends of PHB.
Poly(R)-HB Copolymer of R-HB Poly(R)-HB polymer
with HA blends
1. It is a homopolymer, 1. These polymeric blends 1. These polymer blends
only the R configuration with incorporation of are formed between
of which displays the HA units improves its PHB and biodegradable
isotactic structure physical properties polymers
2. Isolation of PHB from 2. High degree of 2. Two different polymers
bacteria exhibits .70% crystallinity structurally homogenous
crystallinity. The 3. Crystalline structure of or heterogeneous in
components present copolymers composition are mixed
within the bacteria are together and an
water insoluble equilibrium is
amorphous structures established
3. Structure of the blend
3. Crystalline structure of P(3HB-3HV) copolymers Miscible [like P(3HB) with
PHB show isodimorphism, PVC] and immiscible
Detected using X-ray two polymer units [P(3HB) with poly
studies cocrystallize together. (e-caprolactone)] blends
Energy calculations based The crystallinity of the are formed depending on
on the intramolecular copolymer was found to whether the two
configuration detected be inversely proportional polymers are existing in
its structure as a left- to the HB content single phase or two
handed 21-helical Single crystals revealed separate phases,
conformation lath shaped morphology respectively
Lath shape crystals are and a lamellar
formed with arrangement
proportionate
monolamellar system
showing optimum
crystallization at
50 C 6 60 C
Okamura and Marchessault Orts et al. (1991), Saito Azuma et al. (1992),
(1967), Yokouchi et al. and Doi (1994), Saito Kumagai and Doi
(1973), and Sudesh et al. et al. (1996), and Abe (1992), Yoshie et al.
(2000) et al. (1998) (1995), and Sudesh et al.
(2000)
HA, Hydroxyalkanoate; HB, hydroxybutyrate; PVC, polyvinylalcohol.
3.2.2 EPS and its composition
EPS is a large molecular polymer mix produced and secreted by microbes outside
their cell (Ates, 2015). They are the construction substrates for aggregates, such as
flocs, granules, and biofilms. Its composition is a combination of carbohydrate
(40% 95%) and noncarbohydrate moieties including proteins (,1% 60%), lipids
(,1% 40%), nucleic acids (,1% 10%), and heteropolymers (More et al., 2014;