Page 321 -
P. 321
310 CHAPTER 11 Analyzing qualitative data
numbered categories intended to represent the full array of possible responses to a
specific question (Lyberg and Kasprzyk, 1997). For studies using theoretical frame-
works, the codes will come from the categories and concepts identified by the theory.
Emergent coding, however, means that the codes are not identified in advance—the
list will emerge as new concepts of interest are found in the source material. A code
list is normally built into a hierarchical structure, containing multiple levels, each
level representing concepts with increasing amounts of detail. Building a code struc-
ture is not an easy task. It requires both extensive knowledge of the existing theories
and literature and a deep understanding of the data collected. Many times, the analyst
needs to make compromises between the theoretical framework and the practical
aspects of the study.
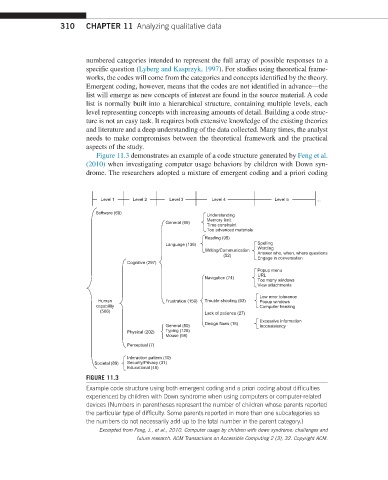
Figure 11.3 demonstrates an example of a code structure generated by Feng et al.
(2010) when investigating computer usage behaviors by children with Down syn-
drome. The researchers adopted a mixture of emergent coding and a priori coding
Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 …
Software (68)
Understanding
Memory limit
General (66)
Time constraint
Too advanced materials
Reading (95)
Language (136) Spelling
Writing/Communication Wording
(52) Answer who, when, where questions
Engage in conversation
Cognitive (297)
Popup menu
URL
Navigation (74)
Too many windows
View attachments
Low error tolerance
Human Frustration (159) Trouble shooting (63) Popup windows
capability Computer freezing
(506) Lack of patience (27)
Excessive information
General (50) Design flaws (18) Inconsistency
Physical (202) Typing (126)
Mouse (59)
Perceptual (7)
Interaction pattern (10)
Societal (89) Security/Privacy (31)
Educational (48)
FIGURE 11.3
Example code structure using both emergent coding and a priori coding about difficulties
experienced by children with Down syndrome when using computers or computer-related
devices (Numbers in parentheses represent the number of children whose parents reported
the particular type of difficulty. Some parents reported in more than one subcategories so
the numbers do not necessarily add up to the total number in the parent category.)
Excerpted from Feng, J., et al., 2010. Computer usage by children with down syndrome: challenges and
future research. ACM Transactions on Accessible Computing 2 (3), 32. Copyright ACM.