Page 61 -
P. 61
46 CHAPTER 3 Experimental design
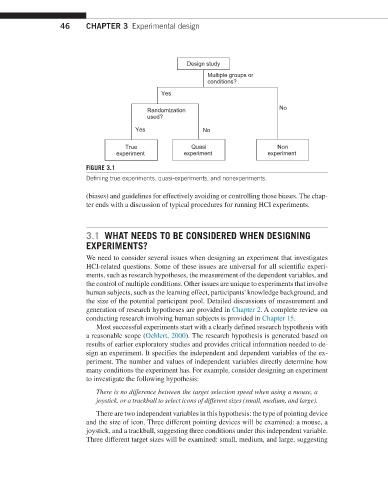
Design study
Multiple groups or
conditions?
Yes
Randomization No
used?
Yes No
True Quasi Non
experiment experiment experiment
FIGURE 3.1
Defining true experiments, quasi-experiments, and nonexperiments.
(biases) and guidelines for effectively avoiding or controlling those biases. The chap-
ter ends with a discussion of typical procedures for running HCI experiments.
3.1 WHAT NEEDS TO BE CONSIDERED WHEN DESIGNING
EXPERIMENTS?
We need to consider several issues when designing an experiment that investigates
HCI-related questions. Some of these issues are universal for all scientific experi-
ments, such as research hypotheses, the measurement of the dependent variables, and
the control of multiple conditions. Other issues are unique to experiments that involve
human subjects, such as the learning effect, participants' knowledge background, and
the size of the potential participant pool. Detailed discussions of measurement and
generation of research hypotheses are provided in Chapter 2. A complete review on
conducting research involving human subjects is provided in Chapter 15.
Most successful experiments start with a clearly defined research hypothesis with
a reasonable scope (Oehlert, 2000). The research hypothesis is generated based on
results of earlier exploratory studies and provides critical information needed to de-
sign an experiment. It specifies the independent and dependent variables of the ex-
periment. The number and values of independent variables directly determine how
many conditions the experiment has. For example, consider designing an experiment
to investigate the following hypothesis:
There is no difference between the target selection speed when using a mouse, a
joystick, or a trackball to select icons of different sizes (small, medium, and large).
There are two independent variables in this hypothesis: the type of pointing device
and the size of icon. Three different pointing devices will be examined: a mouse, a
joystick, and a trackball, suggesting three conditions under this independent variable.
Three different target sizes will be examined: small, medium, and large, suggesting