Page 313 - Robot Builder's Bonanza
P. 313
282 MOUNTING MOTORS AND WHEELS
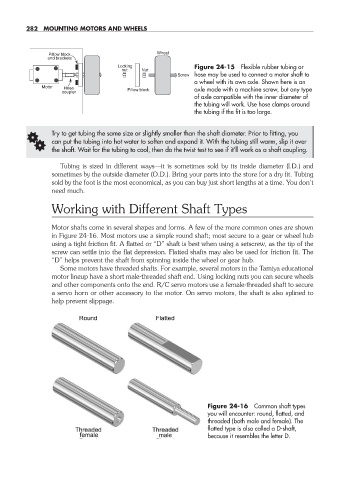
Pillow block Wheel
and brackets
Locking Figure 24- 15 Flexible rubber tubing or
nut Nut
Screw hose may be used to connect a motor shaft to
a wheel with its own axle. Shown here is an
Motor Hose axle made with a machine screw, but any type
coupler Pillow block
of axle compatible with the inner diameter of
the tubing will work. Use hose clamps around
the tubing if the fit is too large.
G Try to get tubing the same size or slightly smaller than the shaft diameter. Prior to fitting, you
can put the tubing into hot water to soften and expand it. With the tubing still warm, slip it over
the shaft. Wait for the tubing to cool, then do the twist test to see if it’ll work as a shaft coupling.
Tubing is sized in different ways— it is sometimes sold by its inside diameter (I.D.) and
sometimes by the outside diameter (O.D.). Bring your parts into the store for a dry fit. Tubing
sold by the foot is the most economical, as you can buy just short lengths at a time. You don’t
need much.
Working with Different Shaft Types
Motor shafts come in several shapes and forms. A few of the more common ones are shown
in Figure 24- 16. Most motors use a simple round shaft; most secure to a gear or wheel hub
using a tight friction fit. A flatted or “D” shaft is best when using a setscrew, as the tip of the
screw can settle into the flat depression. Flatted shafts may also be used for friction fit. The
“D” helps prevent the shaft from spinning inside the wheel or gear hub.
Some motors have threaded shafts. For example, several motors in the Tamiya educational
motor lineup have a short male- threaded shaft end. Using locking nuts you can secure wheels
and other components onto the end. R/C servo motors use a female-threaded shaft to secure
a servo horn or other accessory to the motor. On servo motors, the shaft is also splined to
help prevent slippage.
Figure 24- 16 Common shaft types
you will encounter: round, flatted, and
threaded (both male and female). The
flatted type is also called a D- shaft,
because it resembles the letter D.
24-chapter-24.indd 282 4/21/11 11:51 AM