Page 107 - Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices
P. 107
86 Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices
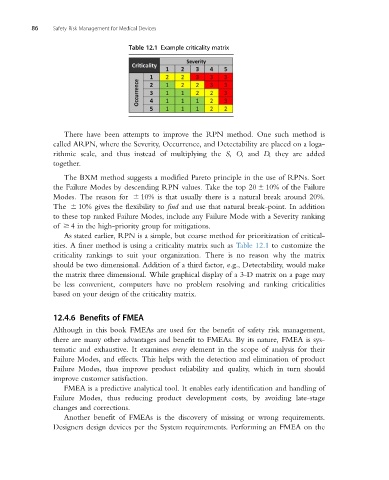
Table 12.1 Example criticality matrix
There have been attempts to improve the RPN method. One such method is
called ARPN, where the Severity, Occurrence, and Detectability are placed on a loga-
rithmic scale, and thus instead of multiplying the S, O, and D, they are added
together.
The BXM method suggests a modified Pareto principle in the use of RPNs. Sort
the Failure Modes by descending RPN values. Take the top 20 6 10% of the Failure
Modes. The reason for 6 10% is that usually there is a natural break around 20%.
The 6 10% gives the flexibility to find and use that natural break-point. In addition
to these top ranked Failure Modes, include any Failure Mode with a Severity ranking
of $ 4 in the high-priority group for mitigations.
As stated earlier, RPN is a simple, but coarse method for prioritization of critical-
ities. A finer method is using a criticality matrix such as Table 12.1 to customize the
criticality rankings to suit your organization. There is no reason why the matrix
should be two dimensional. Addition of a third factor, e.g., Detectability, would make
the matrix three dimensional. While graphical display of a 3-D matrix on a page may
be less convenient, computers have no problem resolving and ranking criticalities
based on your design of the criticality matrix.
12.4.6 Benefits of FMEA
Although in this book FMEAs are used for the benefit of safety risk management,
there are many other advantages and benefit to FMEAs. By its nature, FMEA is sys-
tematic and exhaustive. It examines every element in the scope of analysis for their
Failure Modes, and effects. This helps with the detection and elimination of product
Failure Modes, thus improve product reliability and quality, which in turn should
improve customer satisfaction.
FMEA is a predictive analytical tool. It enables early identification and handling of
Failure Modes, thus reducing product development costs, by avoiding late-stage
changes and corrections.
Another benefit of FMEAs is the discovery of missing or wrong requirements.
Designers design devices per the System requirements. Performing an FMEA on the