Page 157 - Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices
P. 157
136 Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices
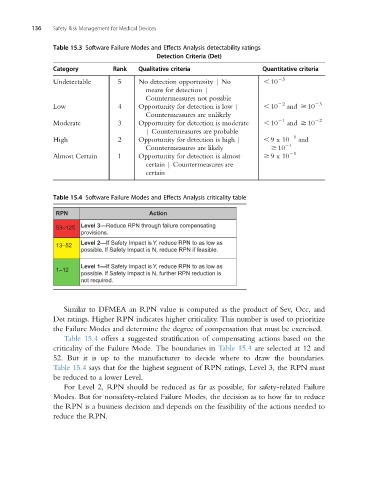
Table 15.3 Software Failure Modes and Effects Analysis detectability ratings
Detection Criteria (Det)
Category Rank Qualitative criteria Quantitative criteria
Undetectable 5 No detection opportunity | No , 10 23
means for detection |
Countermeasures not possible
Low 4 Opportunity for detection is low | , 10 22 and $ 10 23
Countermeasures are unlikely
Moderate 3 Opportunity for detection is moderate , 10 21 and $ 10 22
| Countermeasures are probable
21
High 2 Opportunity for detection is high | , 9x10 and
Countermeasures are likely $ 10 21
21
Almost Certain 1 Opportunity for detection is almost $ 9x10
certain | Countermeasures are
certain
Table 15.4 Software Failure Modes and Effects Analysis criticality table
RPN Action
53–125 Level 3—Reduce RPN through failure compensating
provisions.
Level 2—If Safety Impact is Y, reduce RPN to as low as
13–52
possible. If Safety Impact is N, reduce RPN if feasible.
Level 1—If Safety Impact is Y, reduce RPN to as low as
1–12
possible. If Safety Impact is N, further RPN reduction is
not required.
Similar to DFMEA an RPN value is computed as the product of Sev, Occ, and
Det ratings. Higher RPN indicates higher criticality. This number is used to prioritize
the Failure Modes and determine the degree of compensation that must be exercised.
Table 15.4 offers a suggested stratification of compensating actions based on the
criticality of the Failure Mode. The boundaries in Table 15.4 are selected at 12 and
52. But it is up to the manufacturer to decide where to draw the boundaries.
Table 15.4 says that for the highest segment of RPN ratings, Level 3, the RPN must
be reduced to a lower Level.
For Level 2, RPN should be reduced as far as possible, for safety-related Failure
Modes. But for nonsafety-related Failure Modes, the decision as to how far to reduce
the RPN is a business decision and depends on the feasibility of the actions needed to
reduce the RPN.