Page 67 - Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices
P. 67
46 Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices
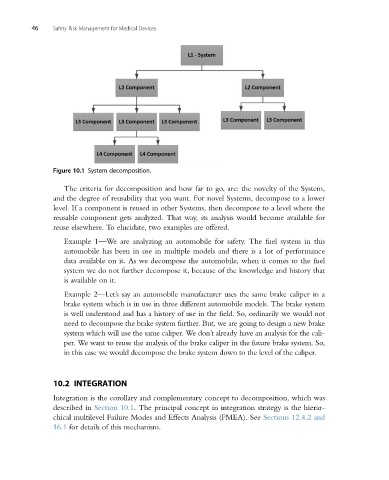
Figure 10.1 System decomposition.
The criteria for decomposition and how far to go, are: the novelty of the System,
and the degree of reusability that you want. For novel Systems, decompose to a lower
level. If a component is reused in other Systems, then decompose to a level where the
reusable component gets analyzed. That way, its analysis would become available for
reuse elsewhere. To elucidate, two examples are offered.
Example 1—We are analyzing an automobile for safety. The fuel system in this
automobile has been in use in multiple models and there is a lot of performance
data available on it. As we decompose the automobile, when it comes to the fuel
system we do not further decompose it, because of the knowledge and history that
is available on it.
Example 2—Let’s say an automobile manufacturer uses the same brake caliper in a
brake system which is in use in three different automobile models. The brake system
is well understood and has a history of use in the field. So, ordinarily we would not
need to decompose the brake system further. But, we are going to design a new brake
system which will use the same caliper. We don’t already have an analysis for the cali-
per. We want to reuse the analysis of the brake caliper in the future brake system. So,
in this case we would decompose the brake system down to the level of the caliper.
10.2 INTEGRATION
Integration is the corollary and complementary concept to decomposition, which was
described in Section 10.1. The principal concept in integration strategy is the hierar-
chical multilevel Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA). See Sections 12.4.2 and
16.1 for details of this mechanism.