Page 210 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 210
CHAP. 16] FLUIDS AT REST 195
The maximum buoyant force on the tank is exerted when the tank is completely submerged. Thus
3
3
F max = (dg) water V = (64 lb/ft )(13.4ft ) = 858 lb
Since the weight of the filled tank is less than 858 lb, it will float.
HYDRAULIC PRESS
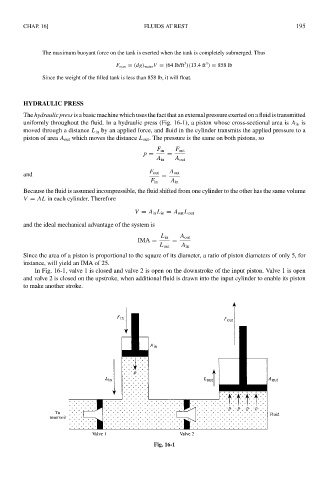
The hydraulic press is a basic machine which uses the fact that an external pressure exerted on a fluid is transmitted
uniformly throughout the fluid. In a hydraulic press (Fig. 16-1), a piston whose cross-sectional area is A in is
moved through a distance L in by an applied force, and fluid in the cylinder transmits the applied pressure to a
piston of area A out which moves the distance L out . The pressure is the same on both pistons, so
F in F out
p = =
A in A out
and F out A out
=
F in A in
Because the fluid is assumed incompressible, the fluid shifted from one cylinder to the other has the same volume
V = AL in each cylinder. Therefore
V = A in L in = A out L out
and the ideal mechanical advantage of the system is
L in A out
IMA = =
L out A in
Since the area of a piston is proportional to the square of its diameter, a ratio of piston diameters of only 5, for
instance, will yield an IMA of 25.
In Fig. 16-1, valve 1 is closed and valve 2 is open on the downstroke of the input piston. Valve 1 is open
and valve 2 is closed on the upstroke, when additional fluid is drawn into the input cylinder to enable its piston
to make another stroke.
Fig. 16-1