Page 232 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 232
CHAP. 18] HEAT 217
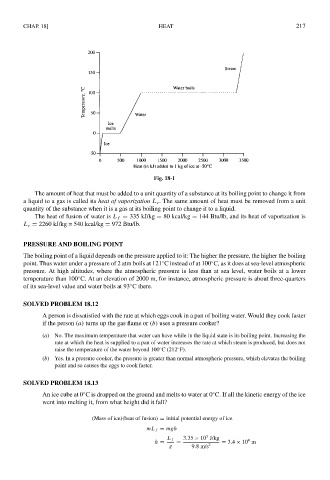
Fig. 18-1
The amount of heat that must be added to a unit quantity of a substance at its boiling point to change it from
a liquid to a gas is called its heat of vaporization L v . The same amount of heat must be removed from a unit
quantity of the substance when it is a gas at its boiling point to change it to a liquid.
The heat of fusion of water is L f = 335 kJ/kg = 80 kcal/kg = 144 Btu/lb, and its heat of vaporization is
L v = 2260 kJ/kg = 540 kcal/kg = 972 Btu/lb.
PRESSURE AND BOILING POINT
The boiling point of a liquid depends on the pressure applied to it: The higher the pressure, the higher the boiling
◦
point. Thus water under a pressure of 2 atm boils at 121 C instead of at 100 C, as it does at sea-level atmospheric
◦
pressure. At high altitudes, where the atmospheric pressure is less than at sea level, water boils at a lower
temperature than 100 C. At an elevation of 2000 m, for instance, atmospheric pressure is about three-quarters
◦
of its sea-level value and water boils at 93 C there.
◦
SOLVED PROBLEM 18.12
A person is dissatisfied with the rate at which eggs cook in a pan of boiling water. Would they cook faster
if the person (a) turns up the gas flame or (b) uses a pressure cooker?
(a) No. The maximum temperature that water can have while in the liquid state is its boiling point. Increasing the
rate at which the heat is supplied to a pan of water increases the rate at which steam is produced, but does not
◦
◦
raise the temperature of the water beyond 100 C (212 F).
(b) Yes. In a pressure cooker, the pressure is greater than normal atmospheric pressure, which elevates the boiling
point and so causes the eggs to cook faster.
SOLVED PROBLEM 18.13
◦
An ice cube at 0 C is dropped on the ground and melts to water at 0 C. If all the kinetic energy of the ice
◦
went into melting it, from what height did it fall?
(Mass of ice)(heat of fusion) = initial potential energy of ice
mL f = mgh
5
3.35 × 10 J/kg
L f 4
h = = = 3.4 × 10 m
g 9.8 m/s 2