Page 285 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 285
270 ELECTRICITY [CHAP. 23
The advantage of knowing the electric field at some point is that we can at once establish the force on any
charge q placed there, which is
F = qE
Force = (charge)(electric field)
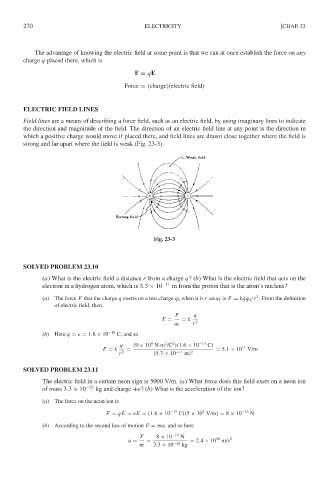
ELECTRIC FIELD LINES
Field lines are a means of describing a force field, such as an electric field, by using imaginary lines to indicate
the direction and magnitude of the field. The direction of an electric field line at any point is the direction in
which a positive charge would move if placed there, and field lines are drawn close together where the field is
strong and far apart where the field is weak (Fig. 23-3).
Fig. 23-3
SOLVED PROBLEM 23.10
(a) What is the electric field a distance r from a charge q?(b) What is the electric field that acts on the
electron in a hydrogen atom, which is 5.3 × 10 −11 m from the proton that is the atom’s nucleus?
2
(a) The force F that the charge q exerts on a test charge q 0 when it is r away is F = kqq 0 /r . From the definition
of electric field, then,
F q
E = = k 2
q 0 r
(b) Here q = e = 1.6 × 10 −19 C, and so
9
2
2
q (9 × 10 N·m /C )(1.6 × 10 −19 C)
11
E = k = = 5.1 × 10 V/m
r 2 (5.3 × 10 −11 m) 2
SOLVED PROBLEM 23.11
The electric field in a certain neon sign is 5000 V/m. (a) What force does this field exert on a neon ion
of mass 3.3 × 10 −26 kg and charge +e?(b) What is the acceleration of the ion?
(a) The force on the neon ion is
3
F = qE = eE = (1.6 × 10 −19 C)(5 × 10 V/m) = 8 × 10 −16 N
(b) According to the second law of motion F = ma, and so here
F 8 × 10 −16 N
10
a = = = 2.4 × 10 m/s 2
m 3.3 × 10 −26 kg