Page 352 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 352
CHAP. 28] ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION 337
The flux through the loop is
2
= BA = (5 × 10 −3 T)(6.4 × 10 −3 m ) = 3.2 × 10 −5 Wb
(b) Since N = 1 for a single turn, we have from Faraday’s law (disregarding the minus sign)
3.2 × 10 −5 Wb
V = N = (1) = 3.2 × 10 −4 V
t 0.1s
SOLVED PROBLEM 28.3
2
A 100-turn coil whose resistance is 6 encloses an area of 80 cm . How rapidly should a magnetic field
parallel to its axis change to induce a current of 1 mA in the coil?
The required emf here is
V = IR = (10 −3 A)(6 ) = 6 × 10 −3 V
and the coil’s area is
80 cm 2 −3 2
A = = 8 × 10 m
(100 cm/m) 2
Since A is constant here,
(BA) B
V e = N = NA
t t
B V e 6 × 10 −3 V
and = = = 0.0075 T/s
2
t NA (100)(8 × 10 −3 m )
THETRANSFORMER
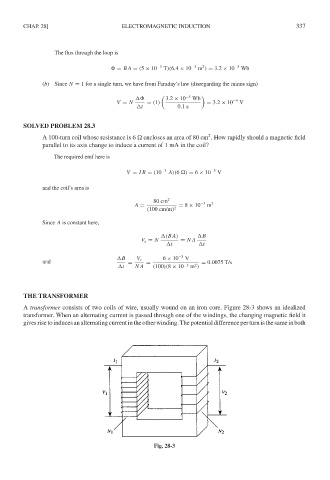
A transformer consists of two coils of wire, usually wound on an iron core. Figure 28-3 shows an idealized
transformer. When an alternating current is passed through one of the windings, the changing magnetic field it
givesrisetoinducesanalternatingcurrentintheotherwinding.Thepotentialdifferenceperturnisthesameinboth
Fig. 28-3