Page 24 - Theory and Problems of BEGINNING CHEMISTRY
P. 24
CHAP. 2] MATHEMATICAL METHODS IN CHEMISTRY 13
and centi. The prefix kilo means 1000 times the fundamental unit, no matter to which fundamental unit it is
attached. For example, 1 kilodollar is 1000 dollars. The prefix milli indicates one-thousandth of the fundamental
unit. Thus, 1 millimeter is 0.001 meter; 1 mm = 0.001 m. The prefix centi means one-hundredth. A centidollar
is one cent; the name for this unit of money comes from the same source as the metric prefix.
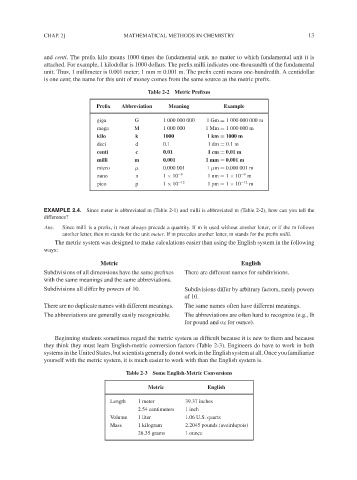
Table 2-2 Metric Prefixes
Prefix Abbreviation Meaning Example
giga G 1 000 000 000 1 Gm = 1 000 000 000 m
mega M 1 000 000 1 Mm = 1 000 000 m
kilo k 1000 1 km = 1000 m
deci d 0.1 1 dm = 0.1m
centi c 0.01 1 cm = 0.01 m
milli m 0.001 1 mm = 0.001 m
micro µ 0.000 001 1 µm = 0.000 001 m
nano n 1 × 10 −9 1nm = 1 × 10 −9 m
pico p 1 × 10 −12 1pm = 1 × 10 −12 m
EXAMPLE 2.4. Since meter is abbreviated m (Table 2-1) and milli is abbreviated m (Table 2-2), how can you tell the
difference?
Ans. Since milli is a prefix, it must always precede a quantity. If m is used without another letter, or if the m follows
another letter, then m stands for the unit meter. If m precedes another letter, m stands for the prefix milli.
The metric system was designed to make calculations easier than using the English system in the following
ways:
Metric English
Subdivisions of all dimensions have the same prefixes There are different names for subdivisions.
with the same meanings and the same abbreviations.
Subdivisions all differ by powers of 10. Subdivisions differ by arbitrary factors, rarely powers
of 10.
There are no duplicate names with different meanings. The same names often have different meanings.
The abbreviations are generally easily recognizable. The abbreviations are often hard to recognize (e.g., lb
for pound and oz for ounce).
Beginning students sometimes regard the metric system as difficult because it is new to them and because
they think they must learn English-metric conversion factors (Table 2-3). Engineers do have to work in both
systems in the United States, but scientists generally do not work in the English system at all. Once you familiarize
yourself with the metric system, it is much easier to work with than the English system is.
Table 2-3 Some English-Metric Conversions
Metric English
Length 1 meter 39.37 inches
2.54 centimeters 1 inch
Volume 1 liter 1.06 U.S. quarts
Mass 1 kilogram 2.2045 pounds (avoirdupois)
28.35 grams 1 ounce