Page 130 - Theory and Problems of BEGINNING CHEMISTRY
P. 130
CHAP. 7] FORMULA CALCULATIONS 119
Ans. 1 mol C 1 mol H
88.8gC = 7.40 mol C 11.2gH = 11.1 mol H
12.0gC 1.008gH
Dividing both numbers of moles by 7.40 yields 1.00 mol C and 1.50 mol H. Multiplying both of these by 2
yields the empirical formula C 2 H 3 . The empirical formula mass is thus 27.0 amu. The number of empirical
formula units in 1 mol can be calculated by using 110 amu for the molecular mass. The number must be
an integer.
110 amu/molecule 4.07 empirical formula units
=
27.0 amu/empirical formula unit 1 molecule
The answer must be integral—in this case 4. If we had used 105 amu or 115 amu, the answer would still
have been closer to the integer 4 than to any other integer. The molecular formula is thus C 8 H 12 .
7.69. A compound has a molar mass of 90.0 g/mol and its percent composition is 2.22% H, 26.7% C, and 71.1% O. What
is its molecular formula?
Ans. H 2 C 2 O 4
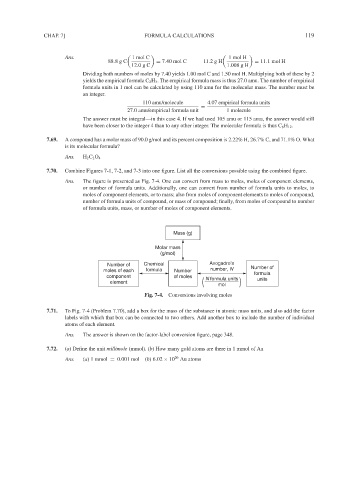
7.70. Combine Figures 7-1, 7-2, and 7-3 into one figure. List all the conversions possible using the combined figure.
Ans. The figure is presented as Fig. 7-4. One can convert from mass to moles, moles of component elements,
or number of formula units. Additionally, one can convert from number of formula units to moles, to
moles of component elements, or to mass; also from moles of component elements to moles of compound,
number of formula units of compound, or mass of compound; finally, from moles of compound to number
of formula units, mass, or number of moles of component elements.
Mass (g)
Molar mass
(g/mol)
Number of Chemical Avogadro’s
moles of each formula Number number, N Number of
formula
component of moles N formula units units
element ( mol )
Fig. 7-4. Conversions involving moles
7.71. To Fig. 7-4 (Problem 7.70), add a box for the mass of the substance in atomic mass units, and also add the factor
labels with which that box can be connected to two others. Add another box to include the number of individual
atoms of each element.
Ans. The answer is shown on the factor-label conversion figure, page 348.
7.72. (a)Define the unit millimole (mmol). (b) How many gold atoms are there in 1 mmol of Au
20
Ans. (a) 1 mmol = 0.001 mol (b)6.02 × 10 Au atoms